When Compete.com launched with credits-based pricing well over a decade ago I felt like a kid in a candy store using their competitive research tool. Recently Compete.com announced they were shutting down, but many of the link analysis & competitive research tools which leverage scraping have also started licensing clickstream data from sources like Clickstre.am & JumpShot.
These sorts of features add a lot of value to traditional keyword tools, as they can highlight the CTR on ads vs organic results & show if people click on anything after they search for a particular term.
When I read Ahref’s recent blog post about integrating clickstream data I got that same kid in a candy store feeling I got when I first used Compete. Some highlights…
- their keyword database contains over 3 billion keywords
- they offer localized search volumes
- searches with clicks vs searches without clicks
- clicks per search
- repeat searches metric
- organic vs ad clicks
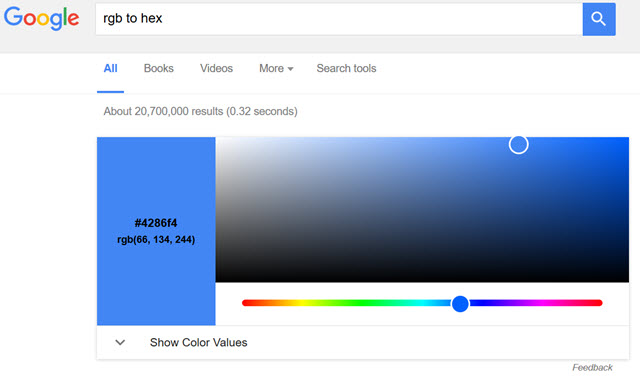
As an example of how the searches with clicks feature is helpful, consider Google’s recently announced RGB conversion feature
In that image you can see how the feature displaces the result set.
What’s cool about the Ahrefs feature is you can also see what sort of impact that feature has on click volumes.
After 1 month, 20% of the searches for [RGB to HEX] no longer had any clicks to an external website.
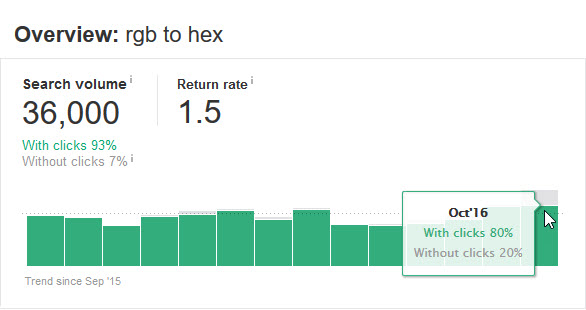
On the second month it looks like the “no click” rate was closer to 7%, so perhaps some of the initial additional search volume was driven by people searching for the related keywords after blogs covered the new feature.
But the nice thing about the feature is you can see how the click rate changes over time as the feature evolves.
In some areas like weather Google ends up dominating most the user behavior with their in-SERP feature.
About half of all weather keyword searches do not click on any listings. And then of those which do click, about 20% of people click on an ad.
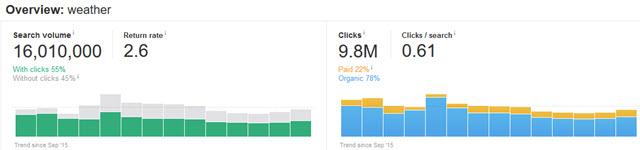
That means the potential organic click volume for that keyword is only about 40% of the initial search volume estimates.
Search results keep getting more interactive features & some of them appear to be click black holes. Literally…
You guys, I’ve discovered a SERP black hole! I’m on #200 suggested PAA for this SERP?! Has anyone else seen an infinite PAA SERP before? pic.twitter.com/YgZDVWdWJ9— Britney Muller (@BritneyMuller) November 23, 2016
Here is a new item comparison feature table.
Has anyone ever seen this giant ‘vs’ featured snippet before? @STATrob @glenngabe @jenstar pic.twitter.com/qaKToKm5C4— Jesse Semchuck (@jessesem) November 22, 2016
As more of the value chain appears in the search results, more of the value chain which formerly appeared on websites disappears. This is true from a wide range of aspects including ad sales, content hosting, ad blocking & brand value.
General Ad Sales
No click into the publisher’s site means no ad revenue for the publisher. Voice search will only accelerate the declines seen from mobile, which shifted user attention away from large screens with many listings to smaller screens with fewer listings & a far higher ad ratio in the search results.
Facebook Instant Articles & Google AMP
Google has already pushed hard to make hotel searches a pay-to-play vertical & yet some publishers are adopting AMP formatting in that vertical. Google is also forcing AMP down publisher’s throats in other verticals like recipes.
@rustybrick New? pic.twitter.com/91TzKfS7tn— Jon Hogg (@ItsHogg) November 24, 2016
If central ad networks host your content then they get better user data for your content than you do as a publisher.
User Tracking, in Aggregate
Increased user tracking depresses premium ad sales & moves value from niche players to broad networks “Whether it’s a third party like Facebook or Google tracking across the web or an ISP leveraging its distribution arm, this is outside of consumer expectations. Importantly to the digital media industry, it also devalues the context and relationship of consumer trust which drives the businesses of premium publishers.”
Ad Blocking
Some large sites like Google or Facebook either pay ad blockers or technically work around them within their apps. By funding ad blockers exempting the search result page from having their ads blocked, Google is ultimately defunding competing ad networks.
Brand Value
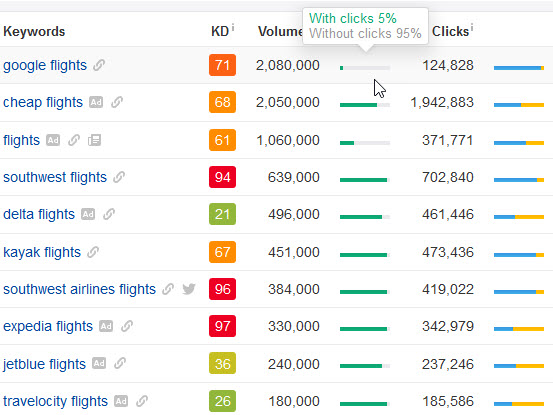
As search results get noisier & more ad heavy, Google is trying to coerce brands into re-buying their pre-existing brand equity. These efforts are effective, as on some branded & navigational searches over half the click volume goes to the ads. Here are a few examples from Ahrefs. The orange bar shows what percent of the SERP clicks are on ads.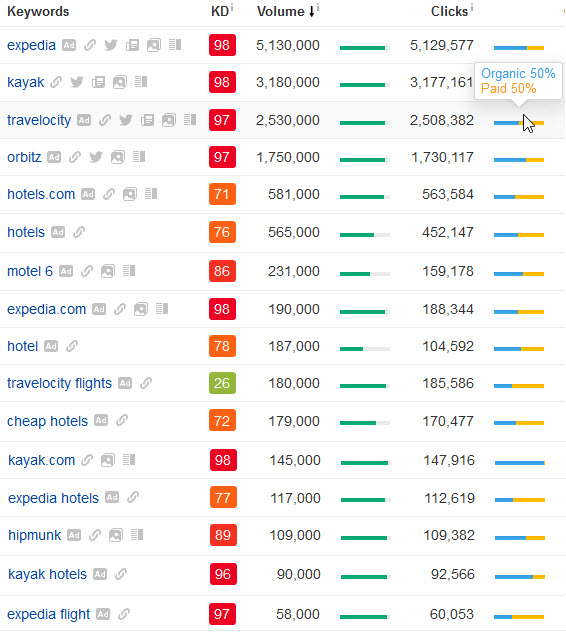
And the above doesn’t even account for…
- Google Maps being an ad-heavy search engine.
- the Google Trips app which prevent searches from happening on Google.
- The mid-tail of travel search on mobile where Google does away with the concept of organic search results.
- Direct booking features complementing traditional AdWords ads & hotel price ads.
- Google buying ITA Software to dominate flight search. Notice the most popular term is Google’s branded term & for the generic term [flights] 72% of people don’t click on any external site while 37% of the remaining 28% of searches click on an AdWords ad.

And almost everyone else in that industry is stuck licensing flight data from Google, as they own ITA Software.
So Google is eating the generic terms, the brand terms, and the search query pool more broadly.
There’s a reason Google’s online travel business is over twice the size of anyone else & has their biggest advertisers seeking more sustainable & more legitimate alternatives.
The biggest travel players are accustomed to Google’s moves and trying their best to adjust and work around them. Missing from this story is the fact that Google’s latest moves are making it nearly impossible for all but the smallest number of consumer travel startups to succeed. — Dennis Schaal
And some of the aggressive stuff carries over into other lines of business outside of travel. Google is also testing large image extensions on AdWords ads on cell phones that don’t leave room for even a second AdWords listing on the screen. When one invests in brand they have to start thinking about how much they are willing to pay Google as an ongoing tithing for their success. Look at the following ads where a competitor bidding on a competing brand drives the brand owner’s official site below the fold.
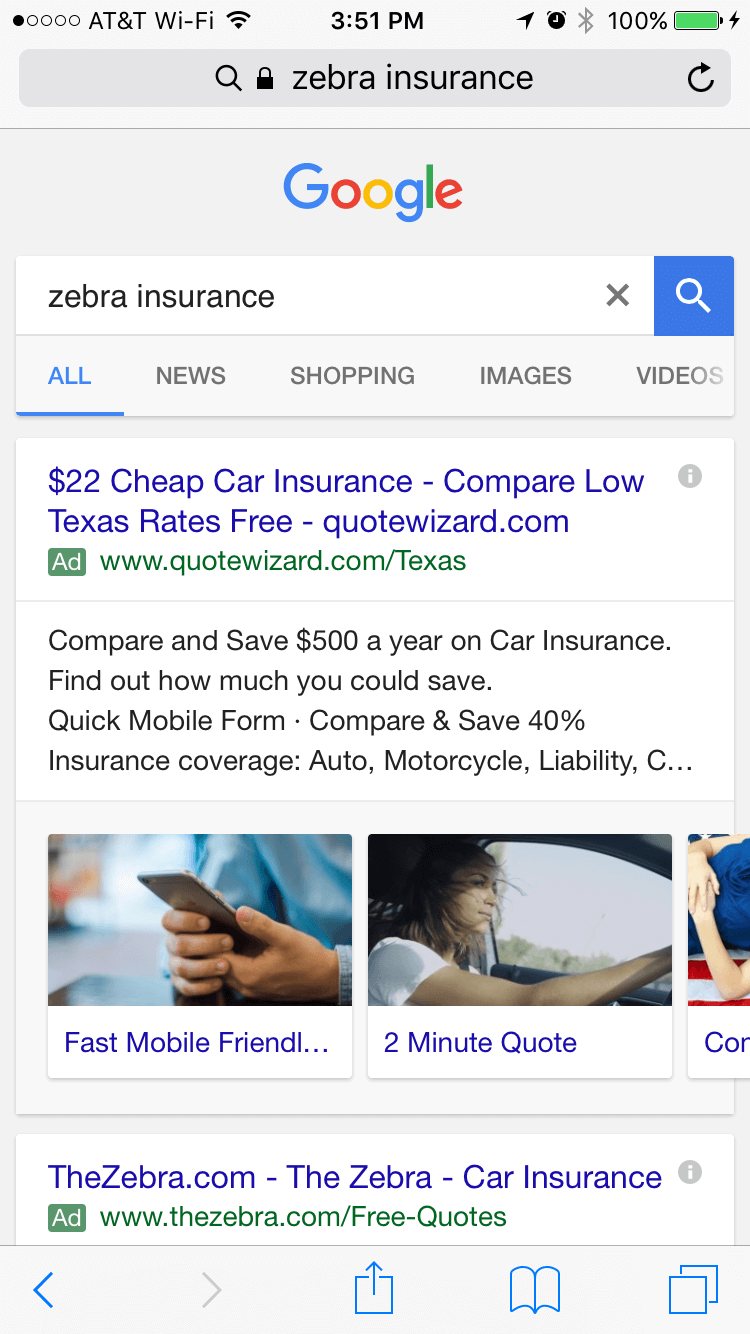
Google is willing to make their results worse (to the point they would consider something that looked like their search result page as an ad-heavy doorway redirect page of spam if hosted by anyone other than themselves) in order to monetize navigational searches.
What’s more, you can’t just opt out & ignore. When brands make agreements to not cross-bid Google has the FTC sue them.
On some high end fashion brands Google lists shopping ads which lead to third party sellers who sell used goods. Quite often counterfeits will also be in the mix. When the counterfeits are destroyed in the first wash, it is the brand owner who was took to the cleaners.
But there’s a solution to that… they can pay Google ever-increasing protection.
@seobook sadly true. I work in the luxury fashion and CTR<15% for nav queries especially w/ sales, forced to buy own brand kw @andrealpar— Giuseppe Pastore (@Zen2Seo) November 26, 2016