Just like when I first watched The Matrix, when I initially heard the term “schema markup,” I was intimidated by the technical know-how I felt I needed to understand it.
However, just like the movie, understanding schema markup isn’t as difficult as you might think.
As a marketer, schema markup is important because you want to make it as easy as possible for search engines to crawl your website.
The easier it is for Google to understand your site, the higher in search engines your website can appear.
Below, let’s review what schema markup is, where to add it, and how it can improve your website’s structure.
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is code you can add to your website that helps search engines return better results for users. Essentially, it gives vital information to search engines to include in your listing that can improve visibility online, as well as click-through rates.
In 2011, top search engines including Google, Yahoo, Bing, and Yandex collaborated to create schema.org, which is a “collaborative, community activity with a mission to create, maintain, and promote schemas for structured data on the Internet, on web pages, in email messages, and beyond.”
Ultimately, schema markup is a form of microdata. According to Wikipedia, “microdata is an HTML specification used to nest metadata within existing content on web pages. Search engines, web crawlers, and browsers can extract and process microdata from a web page and use it to provide a richer browsing experience for users.”
For instance, schema markup will create an enhanced description — sometimes referred to as a rich snippet — which will appear in search results.
As a result of using microdata, your website’s structure will be simple and easy for search engines to crawl, making it easier to appear higher in search results.
Schema Markup Examples
Schema markup can include ratings, reviews, events, and more. You can use schema markup to include important information in your listing on search engines like Google and Yahoo. This will make it easier to show up in search results’ featured snippets. For example, if you sell a product, you can include the star rating in your listing.
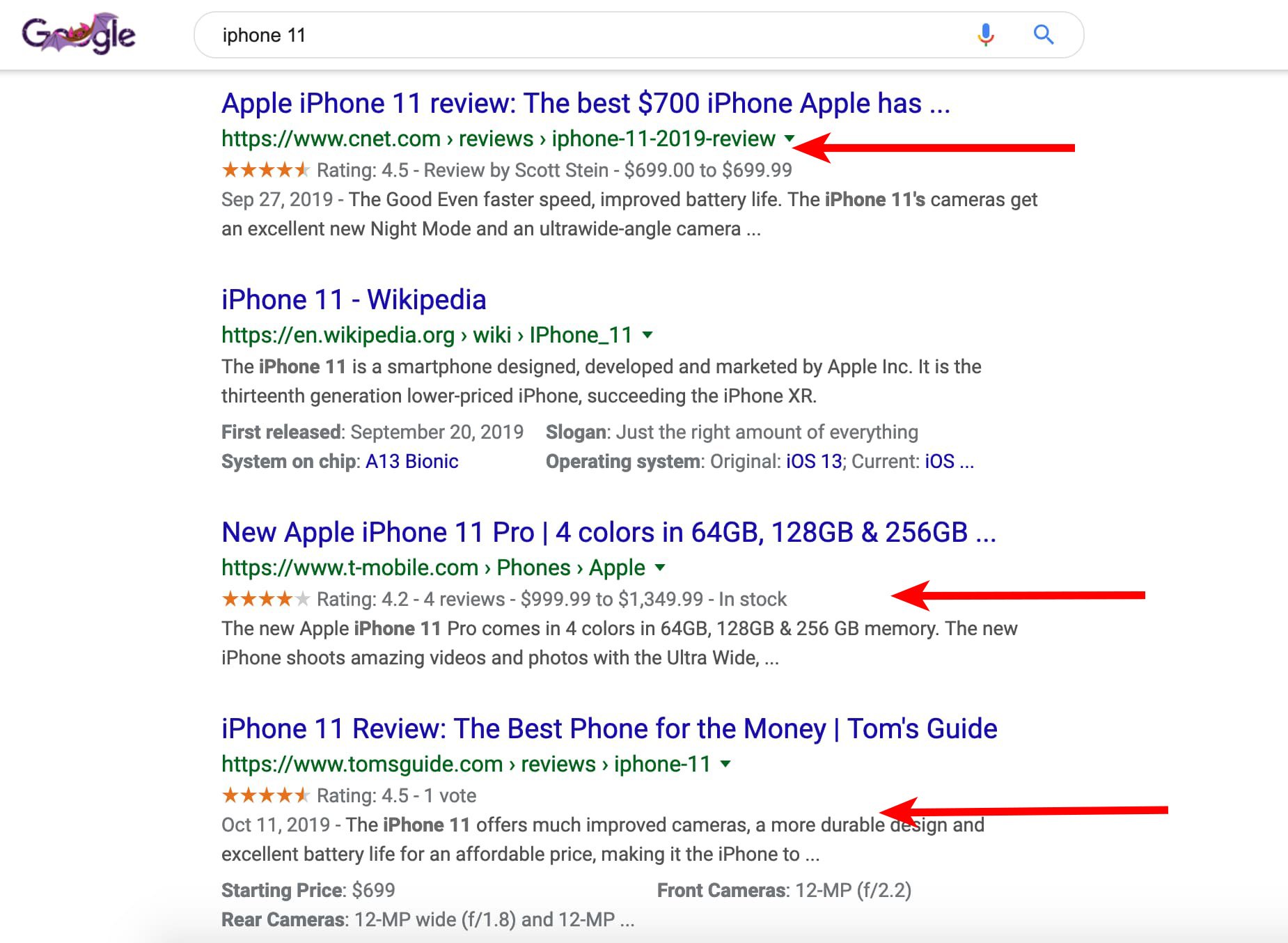
Below is an example of a search engine results page featuring listings with and without schema markup data. As you can see, three of the top four results for the iPhone 11 have schema markup data including ratings, reviews, and price.
Although T-Mobile and Tom’s Guide are the third and fourth listing down, using schema markup microdata can improve its click-through-rate. Plus, it helps the listing stand out from the rest.
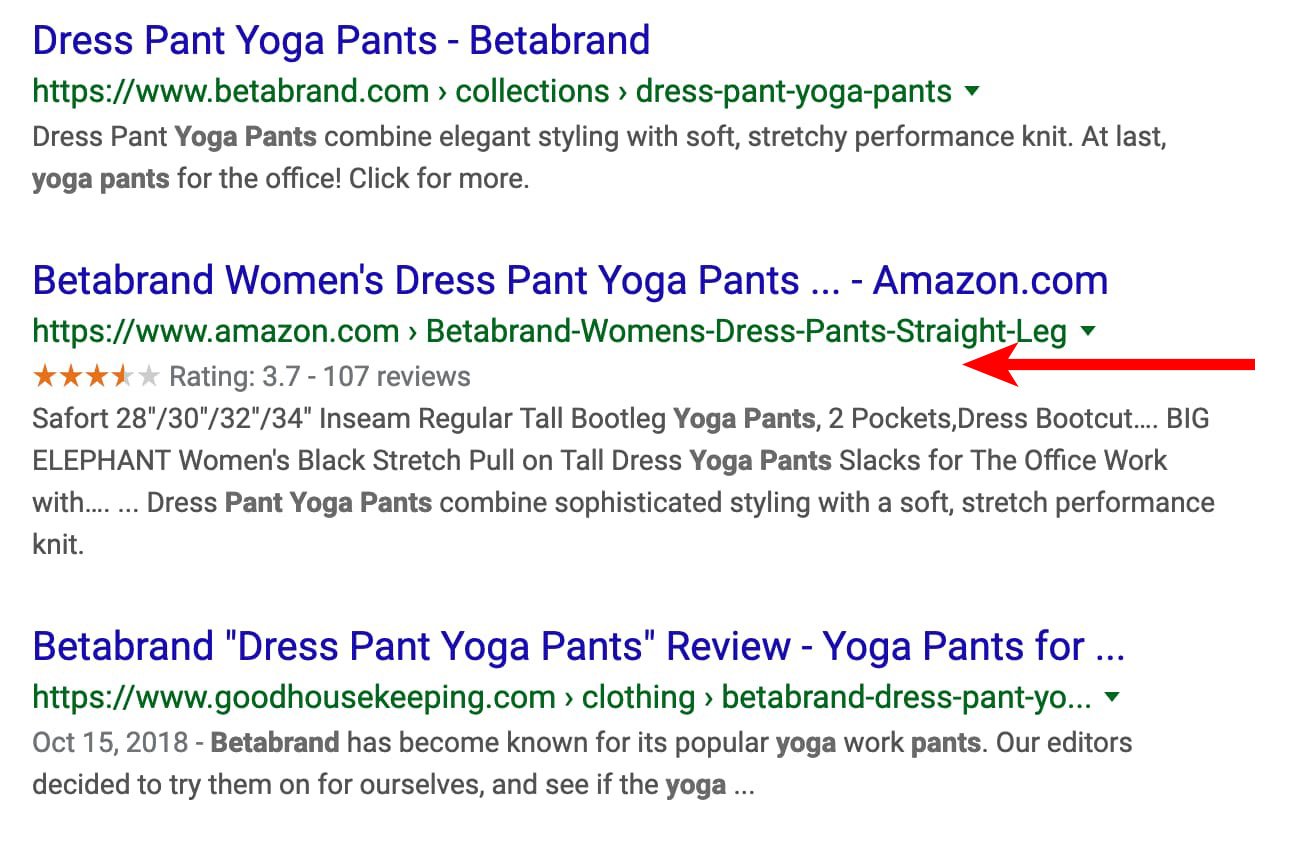
 In the example below, there are three listings for Betabrand yoga pants on Google. The ones from Betabrand and Good Housekeeping don’t include additional information.
In the example below, there are three listings for Betabrand yoga pants on Google. The ones from Betabrand and Good Housekeeping don’t include additional information.However, the one from Amazon includes ratings and reviews.
Again, including this type of information helps search engines provide more information that can persuade users to click on your listing.
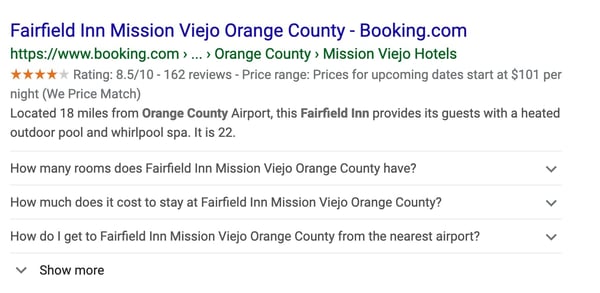
 In the example below, you can see Booking.com used schema markup to include ratings, reviews, price, and Frequently Asked Questions for an Orange County hotel. In their listing, they include a drop-down, answering questions a user might have.
In the example below, you can see Booking.com used schema markup to include ratings, reviews, price, and Frequently Asked Questions for an Orange County hotel. In their listing, they include a drop-down, answering questions a user might have.If someone is searching for and might be staying in that hotel they can learn how close it is to the airport, the average cost, and the ratings.
Where to Add Schema Markup
You can add a variety of microdata depending on your service or product.
For example, you can include:
- Reviews
- Star ratings
- Pricing
- Availability
- Events
- Location
- Price range
- Payment options
- Store hours
The options are endless. No matter what service or product you sell, you can use schema markup to enhance your search engine listings.
So, how do you add schema markup to your site?
The process is actually pretty simple.
Step 1: Go to Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
Step 2: Select the type of listing you want to add schema markup to. Then, copy and paste the URL in the form field.
Step 3: Add schema markup data on the right pane by filling in the information you want to show up.
Step 4: Hit “Create HTML” button.
Step 5: Copy and paste the yellow, highlighted code. This is your schema markup code. Alternatively, you can hit the “Download” button to grab the code.
Step 6: Paste the code into your content management system.
Once you’ve gone through this process, you’ll want to then test your schema markup to make sure it shows up correctly in search engines. Below, we’ll review how to test your listing.
Schema Markup Tester
Now that you’ve added the schema markup code to your site, it’s time to test it out. You can do this by using the Google Structured Data Testing Tool.
You can test your schema markup two ways: by URL or code.
To test the URL, all you need to do is copy and paste the URL of the webpage you want to see. Then, the tool will showcase a preview of your listing.
To test the code, you can copy and paste the code the structured data markup tool generated for you. Again, a preview of your listing will appear.
While schema markup may seem technically intimidating, it’s actually a simple process. By using schema markup code, you can increase the visibility of your search engine listings and improve click-through-rates.

