You know how Google says you can’t “fix” your way back to position one? That seems unhelpful but it’s actually useful. It helps one understand what not to waste time on. In my opinion, based on my experience, once you know what not to focus on, it will help you understand more productive areas to focus on.
Things to Fix
According to Google, fixing things won’t help you recover. What does that mean?
It may mean that the traditional things SEOs focus on, mainly technical SEO, have little to do with fixing an update that’s highly likely about relevance.
Some SEOs say that every site they audit that has experienced ranking drops has serious issues with technical SEO factors.
Well, that statement loses impact when you consider the fact most sites technically challenged, particularly with page speed. Did you know that page speed is getting slower?
If you check the top ranking sites, they’re probably not doing well with technical SEO factors yet ranking in the top three regardless.
Page Speed
Page speed is important. But even Google’s own John Mueller has indicated that page speed is one of many ranking factors, many of which are more important than page speed. If you have any doubt, check out how slow the top ranking sites are for any particular query.
In a Webmaster Hangout, a publisher was frustrated because his site was optimized for speed. But he was being outranked by slower web pages.
The publisher asked John Mueller:
“What about speed for the mobile version? …Why are a lot of the top sites still so slow?”
And John Mueller answered:
“…the good part is that we have lots of ranking factors. So you don’t have to do everything perfect.
But that also means that you run across situations like this where you say, Google says speed is important but the top sites here are not so fast therefore it must not be important.
So for us it is definitely important. But that doesn’t mean it kind of overrides everything else.”
That part about “overrides everything else” is important because in my opinion it alludes to things like relevance, popularity signals and other factors related to understanding what users want to see when they make a search query.
It simply does not make sense to rank a site lower because of slow speed if that site is the most relevant answer to a user’s search query. The number one goal is to satisfy the search query.
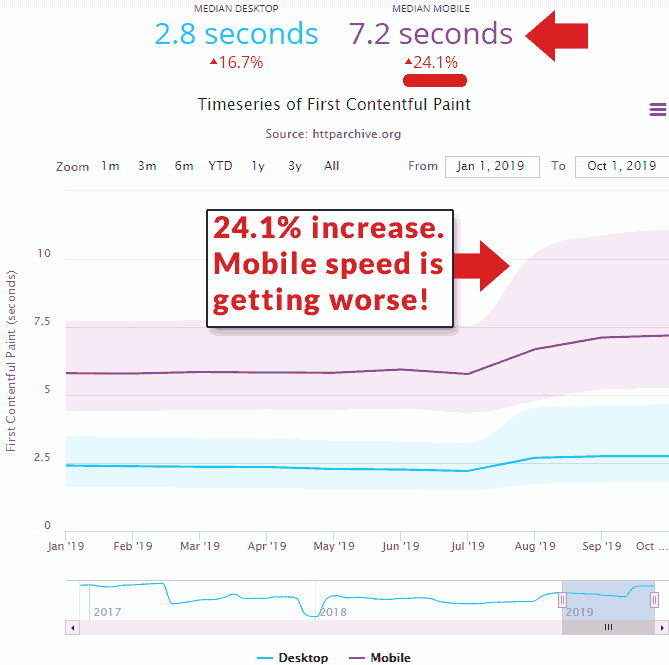
The fact is that mobile sites are getting slower. The following graph from HTTP Archive shows that the first contentful paint has actually increased by 24.1% from January 2019 to October 2019.

Anyone who tells you that a site lost rankings because of page speed, fact check them by checking the page speed of competitors who are outranking you. Odds are that their page speed may be similar to yours.
I am not minimizing page speed. Page speed is super important for conversions, ad clicks and keeping visitors engaged.
I’m just saying that as a ranking factor, page speed has been vastly overrated.
Junk Links and Disavows
Every site that is top ranked has junk links. Google ignores paid links and junk links because what’s important is if a web page answers a search query. So if the page is good then Google will still rank the web page.
Yes, paid links may boost a normal site for. But after a short period of time, from days to months, those links stop working and the site drops back to where it formerly ranked. That’s an example of how Google ignores links.
In my opinion, based on experience helping sites recover from penalties, a manual penalty happen when certain thresholds of different spam signals are reached.
For example, a normal site that receives thousands of keyword-optimized anchor text links from other normal sites may raise flags and be subjected to a hand review.
Off topic keyword-optimized anchor text links from spam sites are ignored by Google. One reason is because the irrelevance of the links to the page that’s being linked to is a reason to not count the link. Another reason is because this fits the statistical average for normal linking patterns.
Rogue link builders have been taking advantage of this loophole for years by paying for links and pointing them at their clients. It’s only after they reach a threshold that the links are flagged and come under review. That’s likely how JC Penney got in trouble eight years ago.
It is a fact that Google ranks sites that have spammy backlinks. Google’s John Mueller is on record saying that Google will ignore spammy links if the content is good enough.
This is the question:
“I see a disturbing amount of link networks and nefarious link building schemes being used… I reported these as suggested but is there anything else that we can do?
This is really frustrating.”
This is John Mueller’s answer:
“…when it comes to competitive areas, what we’ll often see is that some sites do some things really well and some sites do some things really bad.
We try to take the overall picture and use that for ranking.
For example, it might be that one site uses keyword stuffing in a really terrible way but actually their business is fantastic and people really love going there, they love finding it in search and we have lots of really good signals for that site.
So we might still show them at number one, even though we recognize they’re doing keyword stuffing.”
The point is that Google is not going to reduce a site’s rankings by 30% or 90% because of links. If people loved the site last week, then Google is still going to rank it #1 this week after an algorithm update.
If your site has suffered ranking declines, it’s highly unlikely the declines are due to random spam links.
Missing Pages and 404 Error Response
404 response codes are normal.
This is what Google’s John Mueller said about 404 response pages:
“…if we check those URLs and see a server error or the Page Not Found error here, then that’s something we’ll tell you about in Search Console. …and that’s fine. …if we check those URLs and see a server error or the Page Not Found error here, then that’s something we’ll tell you about in Search Console. …and that’s fine. …It’s not something you need to worry about.”
Why Do Sites Lose Rankings?
If you read and listen to what Googler’s say, one thing becomes evident: Google wants to match relevant web pages to search queries. Google stated that the recent BERT update was about better understanding of 10% of English language search queries. That’s about relevance.
The reason Google changed the nofollow attribute from a directive (something Google is obligated to obey) to a hint (something Google can ignore if it wants) is because of relevance.
Google’s Gary Illyes stated that the reason was because Google wants to use the nofollow link signal to improve relevance.
My question to Gary Illyes:
“Is Google’s motivation for this change because Google wants to strengthen the link signal in order to get better search results?”
The following answer was relayed to me via a friend (Kenichi Suzuki) in Japan who asked Gary Illyes:
“Yes. They had been missing important data that links had, due to nofollow. They can provide better search results now that they consider rel=nofollowed links into consideration.”
Another example is last year’s poorly named “Medic” update. This update affected more than just medical sites. Many health related sites lost rankings. The reason appears to be because Google decided that users preferred science based web pages instead of pages about non-medical “natural” type remedies.
That’s a relevance issue. The so-called “Medic” update appeared to be clearly about relevance issues, not about author bios or “expertise.”
Takeaway
There have been two recent changes at Google that should be considered.
- The first one was changing the nofollow attribute from a directive to a hint. That means that many more links are being used as ranking factors.
- The second important change is BERT, which is said to affect 10% of search queries, including things like featured snippets. The featured snippets aspect alone can account for some traffic declines.
Both of those factors, nofollow links and BERT are about relevance. I am not saying BERT and nofollow links are the update
It could very well be there are other factors that are affecting rankings.
Relevance and Technical Issues
Fixing technical SEO factors is important. But identifying relevance issues may be even more important in order to recover from a ranking decline. Almost every update that Google has rolled out had “relevance” as a factor.
A few updates were about other factors, like Google’s “speed” update that added site speed as a (soft) ranking factor. And when that was the case, Google notified publishers. Same with the Panda Update (content related) and the Penguin update (links related).
In general, if Google isn’t talking about it, in my opinion based on my experience helping sites recover, it’s helpful to start looking at relevance.