
Unlike content marketing (which is centuries old), SEO is a very new discipline. It has been around for just a couple decades, and it quickly became the primary digital focus for many marketers.
Yet, SEO cannot exist without content, and I am happy to report that the search industry has reached maturity when it goes back to basics: recognizing that content is the most important and fundamental part of the marketing puzzle. Now, with SEO maturing so quickly, there are still many misconceptions and misunderstandings around it. Those misconceptions may impact the content marketing process in a not-so-positive way.
Let’s clear things up a bit:
1. SEO Has Become Much More Integrated and Diverse
SEO used to be standalone: no one had any idea what SEOs were doing and how they got pages ranked. Many SEOs would ignore very important digital marketing aspects, including user experience, brand building, etc. The only purpose was to get a page ranked.
These days it’s finally different: SEO is just one element of success. It’s next to impossible to achieve high rankings without building authority and brand awareness, or without ensuring users are going to have a good experience using the site.
#SEO is just one element of digital success. It’s next to impossible to achieve high rankings without building authority and brand awareness, and delivering a great user experience Click To Tweet
Google has taken all of that in the account: they monitor how users interact with a website, how satisfied they are, and how quickly they find answers when landing on a page from search results. Google has made trust and authority important ranking signals.
As a result, there are fewer and fewer companies that focus on a single component of SEO (like link building) or even just SEO. Most companies are offering full-package internet marketing services that include video production, social media marketing and usability. Some companies even go beyond that by offering “integrated marketing services”. talkingAds, a company that oversees the entire marketing plan for its clients, describes the benefits of this approach in much detail and why it’s crucial for businesses:
The important elements in marketing communication are advertising, personal selling, direct marketing, public relations, website communication, sponsorship and social media presence. A disjointed approach isolates these functions that lead to non-consistency of brand value to the end-user.
Lonely Brand offers a few examples of integrated marketing and defines it as follows:
Integration means mapping your strategy to the reality of the customer.
Do you see where keyword research and data analytics fits in here? Exactly: like any other marketing channel, SEO goes back to the customer. If the customer is pleased, Google will catch on that.
2. SEO Is No Longer Focused on Exact-Match Strings
As an SEO, with a huge passion for writing, I think this is the most welcome development as far as I am concerned.
Remember the days when writers were given one phase and forced to use it a certain number of times within a copy?
Well, those days are happily over.
Search engines have moved beyond so-called “keyword strings”. They can now understand concepts, entities and topics. You can see the trend all over Google search results pages.
Try searching for something specific, like [good hiking spots], now scroll through those results. A few years ago, Google would focus on the exact match [good hiking spots] and show you results that have the exact phrase in their title tags. Now they’re much smarter than this. You’ll see a good mix of phrases that express the same thing, i.e. places nearby that are great places to hike.
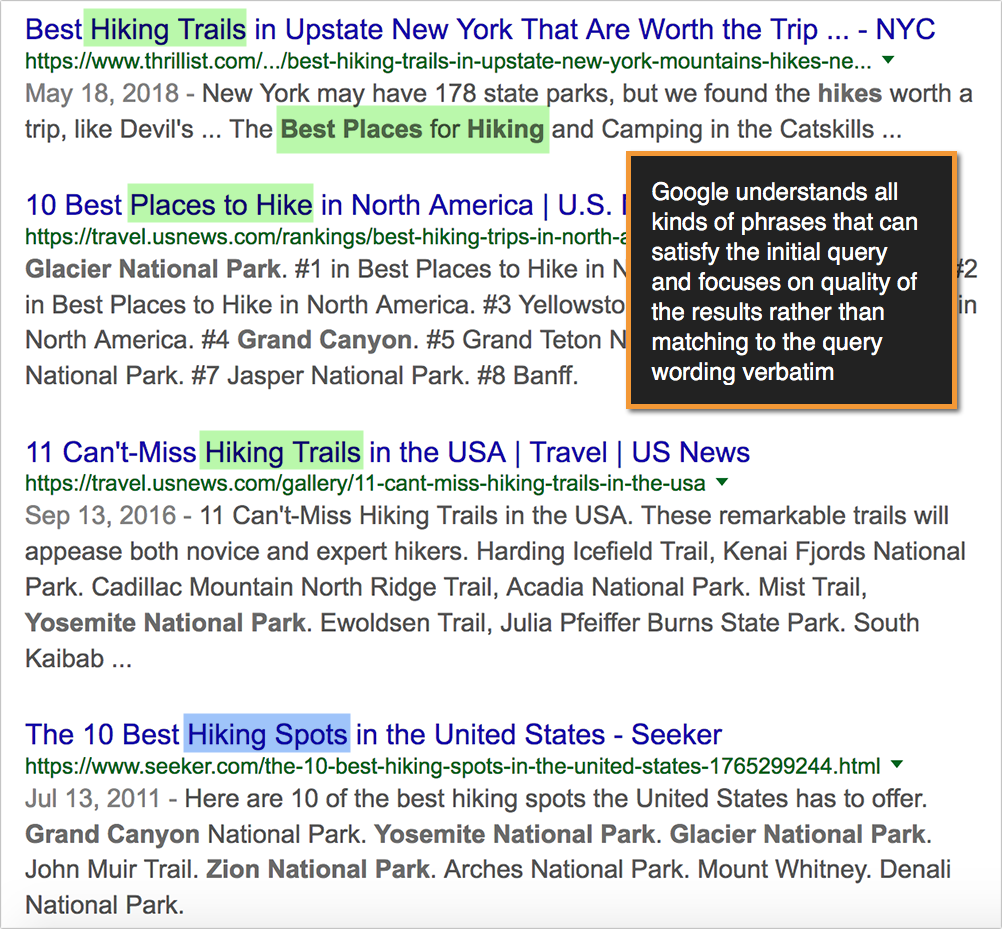
Google understands all kinds of phrases that can satisfy the initial query and focuses on the quality of the results rather than matching to the query wording verbatim. Quality and depth of content have become much more important than the exact keyword you put on the page.
Action item: Use keyword tools that don’t focus on exact-match and give you a variety of phrases that can inspire more content angles. Ubersuggest is a great option. It’s open, completely free and offers a good selection of filters as well as a quick analysis of current search results for each query. But the best part is: it generates all kinds of keywords that relate to the term you type in.
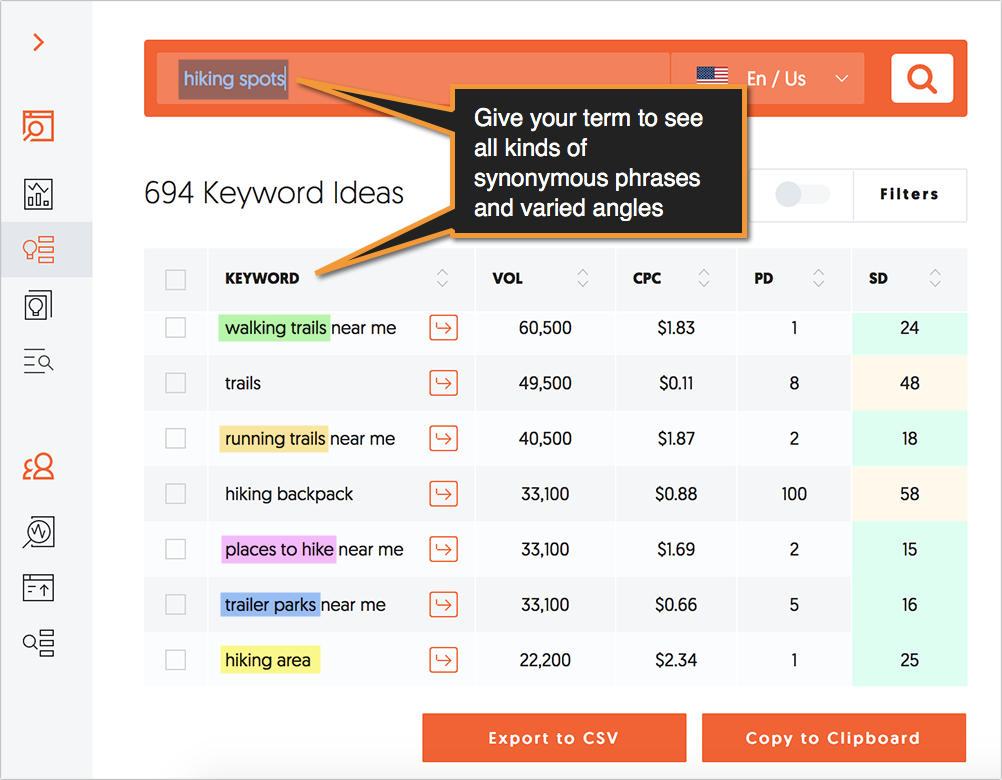
Try it yourself: type in your term to see all kinds of synonymous phrases and varied angles.
For another example of how search engines have advanced, look at how Google clusters topics by entities (i.e. “brands”) they know about. If you type something generic, like [how to set up call forwarding], Google would know that the query may be multi-faceted, so it will allow you to quickly browse through a more specific answer right within the featured snippet:
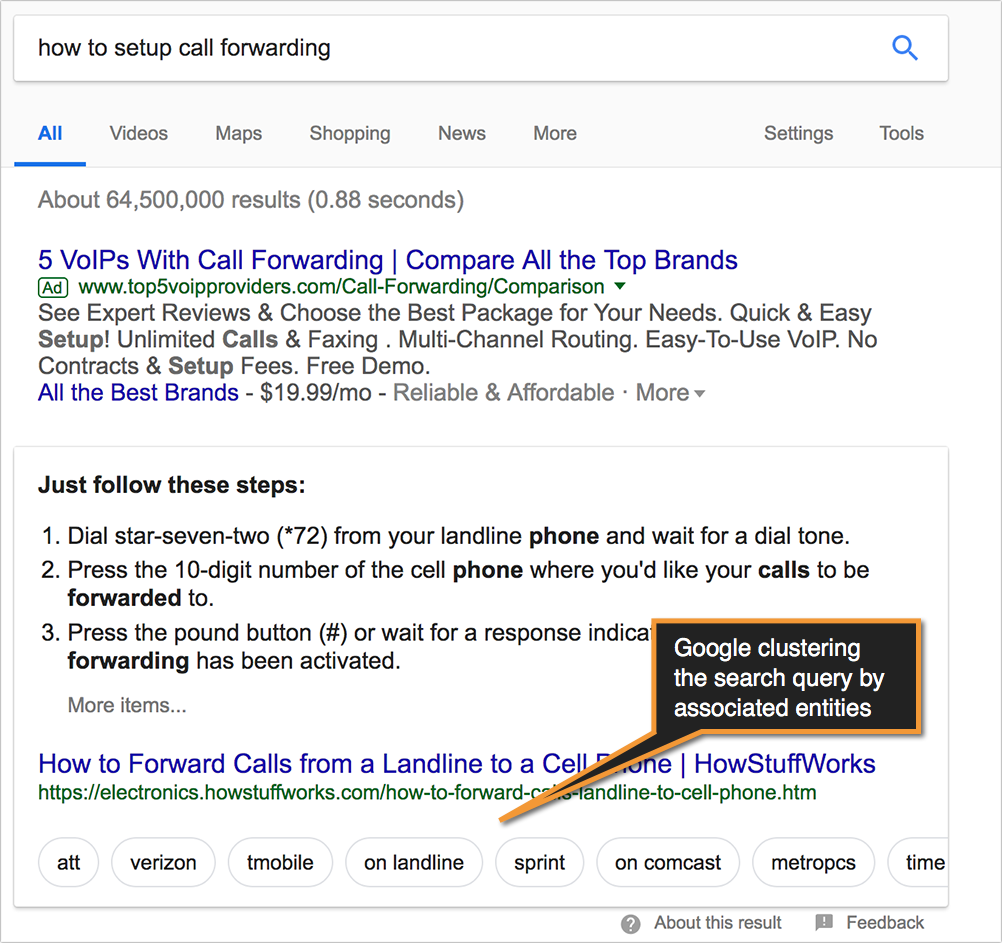
Action item: When working on content, make sure you understand related subtopics and subcategories that need to be included in your article.
Use Serpstat to cluster your keyword lists by topics. They use Google results for each keyword in a list to identify how closely queries are related based on how many overlapping URLs there are ranking for each set of keywords. The fact that Serpstat isn’t using a traditional clustering technique (i.e. the one that groups phrases based on a common core term in each phrase) makes it a much smart and more up-to-date option to use nowadays:
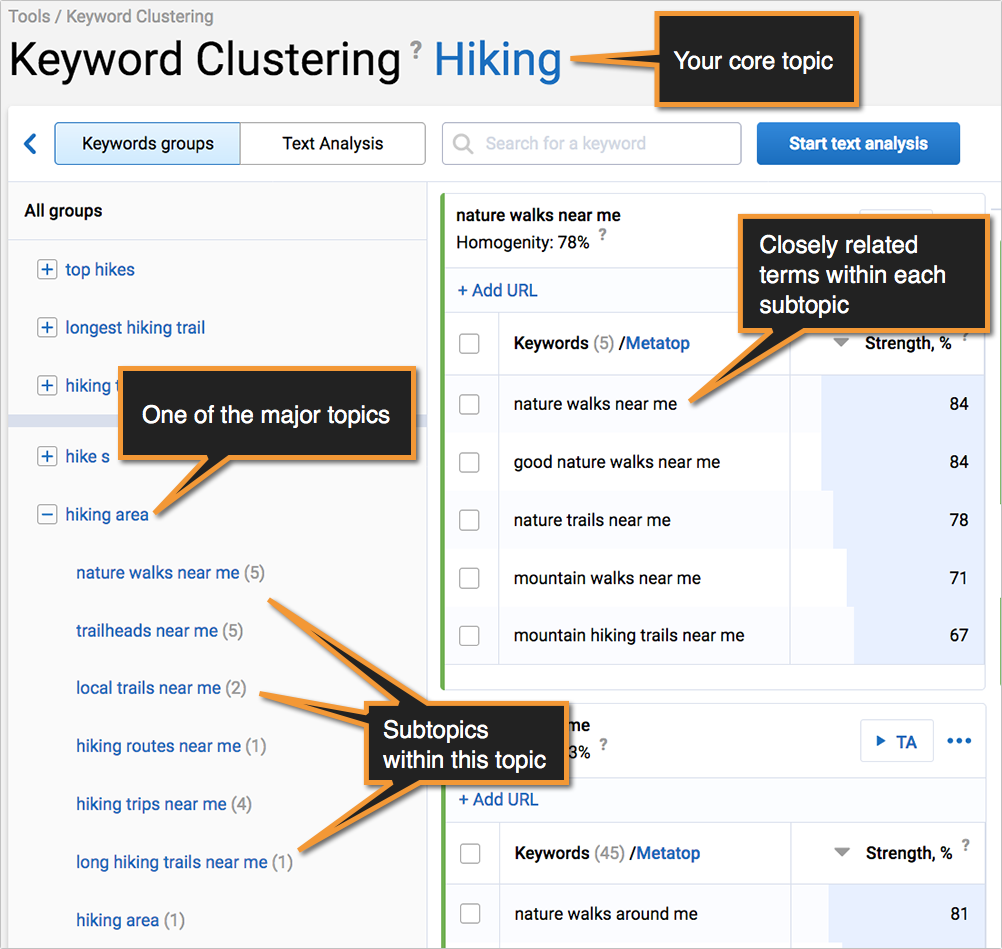
[Read more about Serpstat’s clustering feature here.]
3. Search Gives Us Lots of Cues
Search has evolved. Google has become smarter at identifying search intent and giving their users exactly what they want. They have become better at identifying peoples’ struggles and serving the best answer within search results. They have learned to find questions behind queries and show their users more options for researching a topic.
The fact that all of that comes up in search results makes it possible for writers to learn more about any topic they are writing about. The key is to learn to see and interpret those cues to create more valuable and better-optimized content.
Let’s try to see that in action:
1. When searching, look at all kinds of “blended” search results that come up.
- Is there a video carousel? That means Google has found users engage with videos more for this particular query, so maybe you need to put one together too,
- Are there image results? That means Google has seen its users look for visual content when searching. Think about which parts of your article you can visualize to make it more appealing and engaging.
- Are there shopping results? This signals of high commercial intent, so your article may not do so well here. How about finding a more informative angle? A product comparison may be a good angle to find, so research more angles.
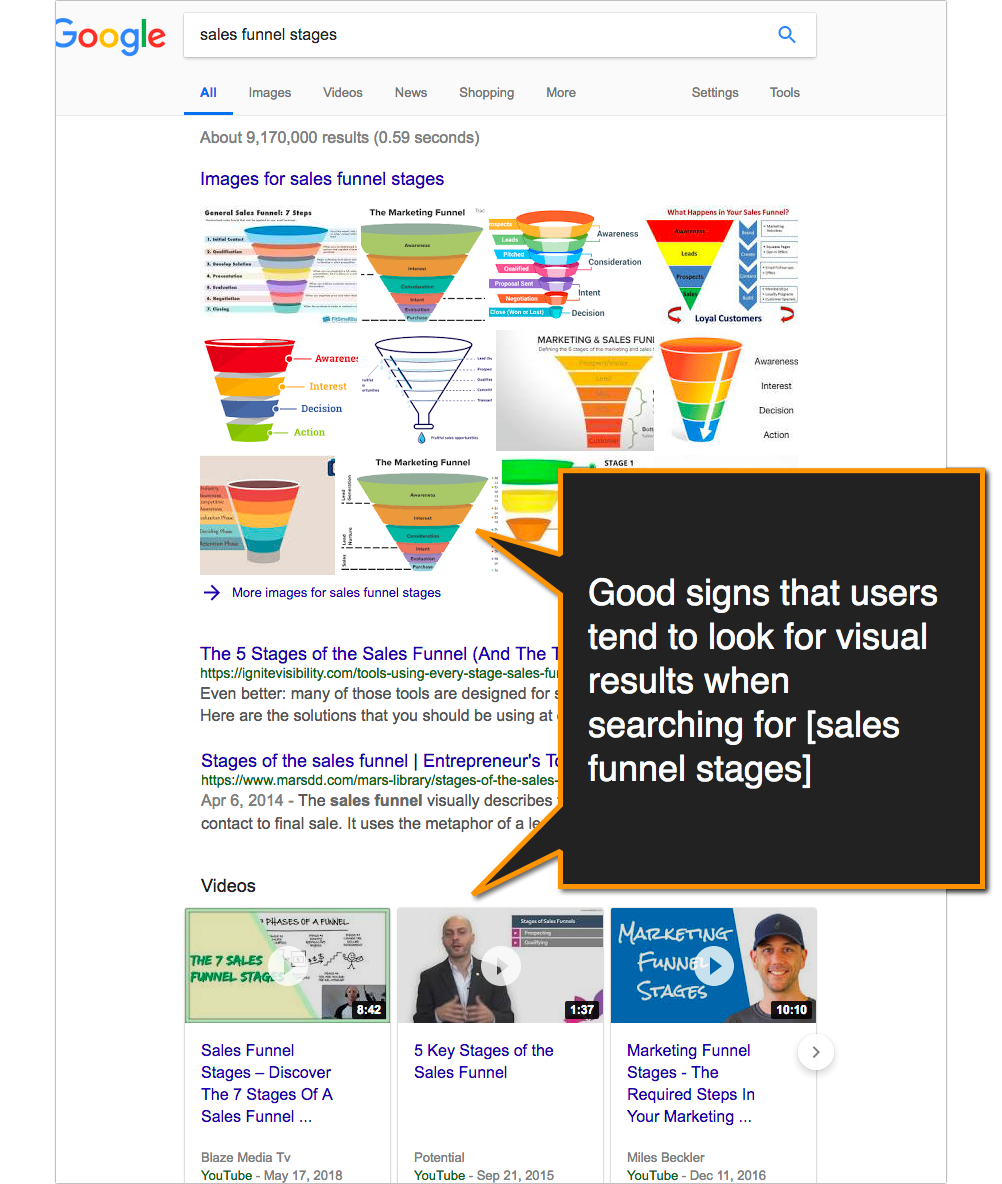
2. When searching, look at “People Also Ask” results.
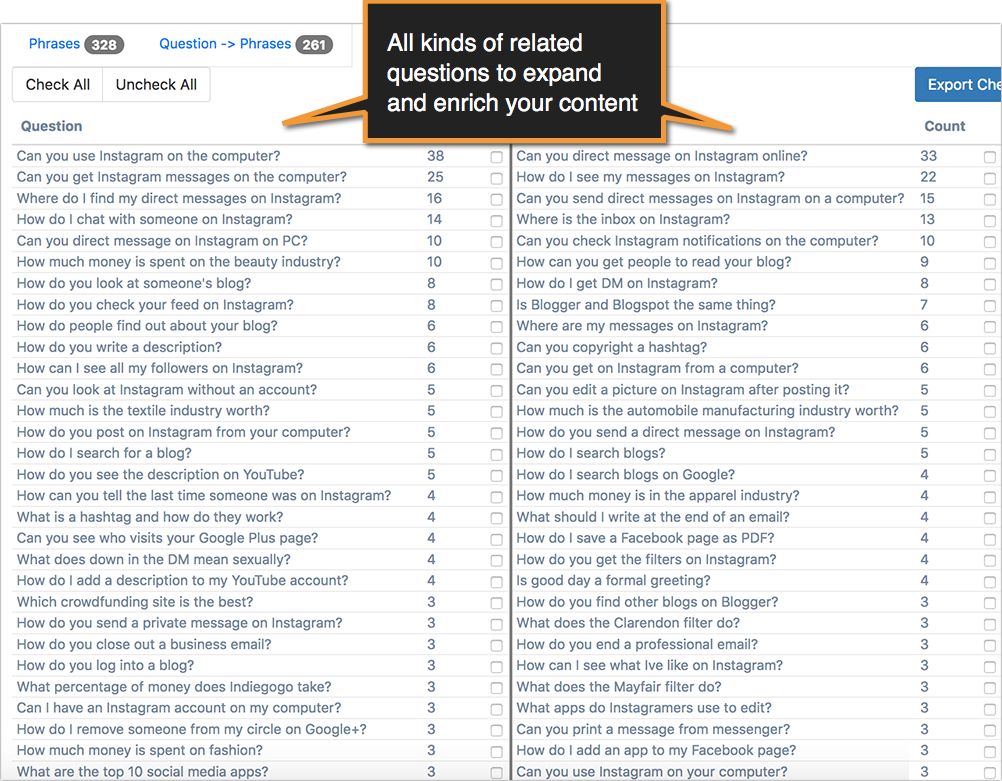
Google’s “People Also Ask” boxes show popular questions based on your query. These provide a goldmine of content inspiration. Click on some of those questions to see more questions show up underneath.
Featured Snippets Tool [Disclaimer: This tool has been developed by Internet Marketing Ninjas, the company I work for] will help you streamline the process. Simply put your domain or the URL of the article that covers a topic you are researching, and it will generate the list of all kinds of questions Google shows for a variety of queries this domain or URL shows up in Google for. You’ll see all kinds of related questions to expand and enrich your content.
3. When searching, pay attention to Google’s Featured Snippets.
Google has gone a long way at learning to understand any web copy and extracting useful information. Look at those featured snippets to learn to better structure your copy to make it easier for Google to understand as well as more useful for your users:
- Define concepts
- Focus on facts and numbers (e.g. if you are describing a tool, explain its pricing)
- Use subheads (especially if you are using questions from the step above)
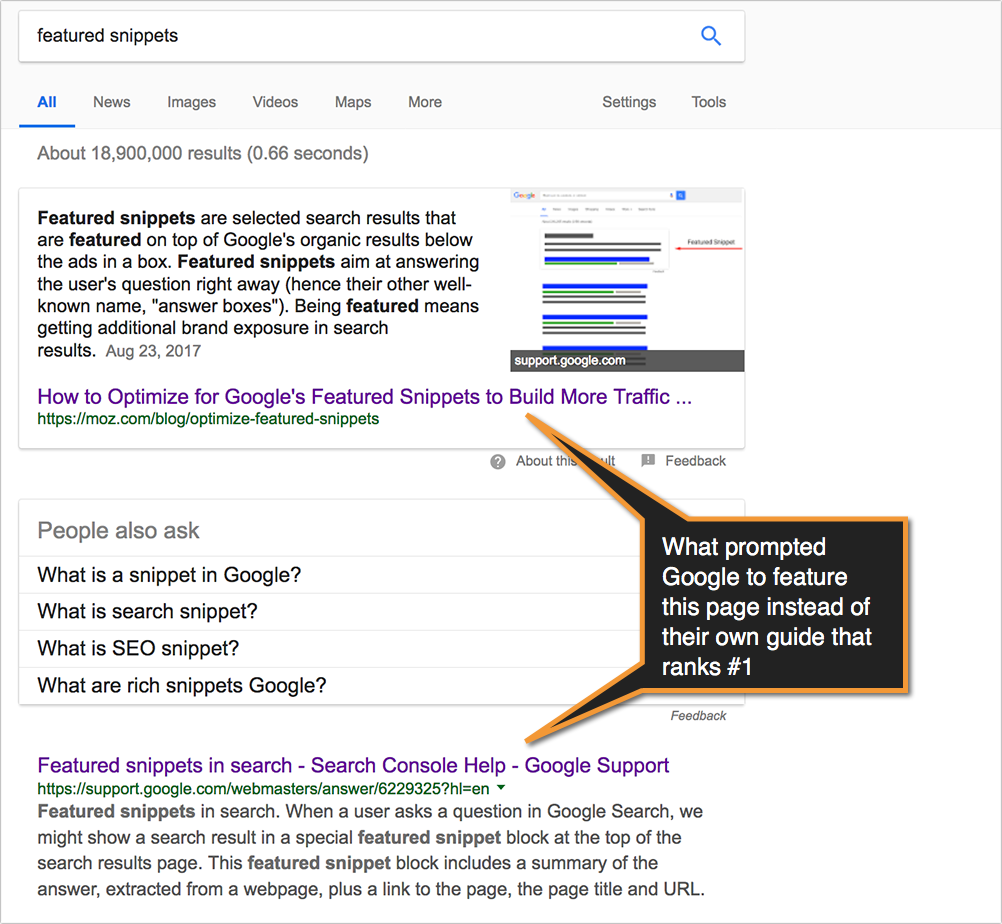
What prompted Google to feature this page instead of their own guide that ranks #1?
These days, instead of forcing artificial copy, Google makes your content better by teaching you to research more, structure better and use a more varied vocabulary.