The blockchain is pretty technical at its core, but essentially it’s a way for digital information to be stored and distributed, but not copied. It is the ultimate peer-to-peer network.
The 90-second Blockchain Breakdown.
Many years ago, music-sharing software Napster pioneered the way for the first of its kind – peer-to-peer file-sharing networks – and, despite being illegal, paved the way for companies like Spotify and Skype.
Here’s a simple way to imagine this. When you edit a document in Microsoft Word, you can’t have your co-worker edit that same document unless you send it to them and ask them to make revisions. Then, if they want you to make revisions to that same document, they’ll have to save their version and send that one to you; only one person can make edits at any given time.
But with Google Docs, multiple people can make edits to the same document, at the same time.
The blockchain is like one “shared” document. It has blocks of identical information that’s stored across its network, so it can’t be controlled by any one person and has no single point of failure. Because of this, the blockchain hasn’t had any problems due to its structure, only human error (i.e. hacking).
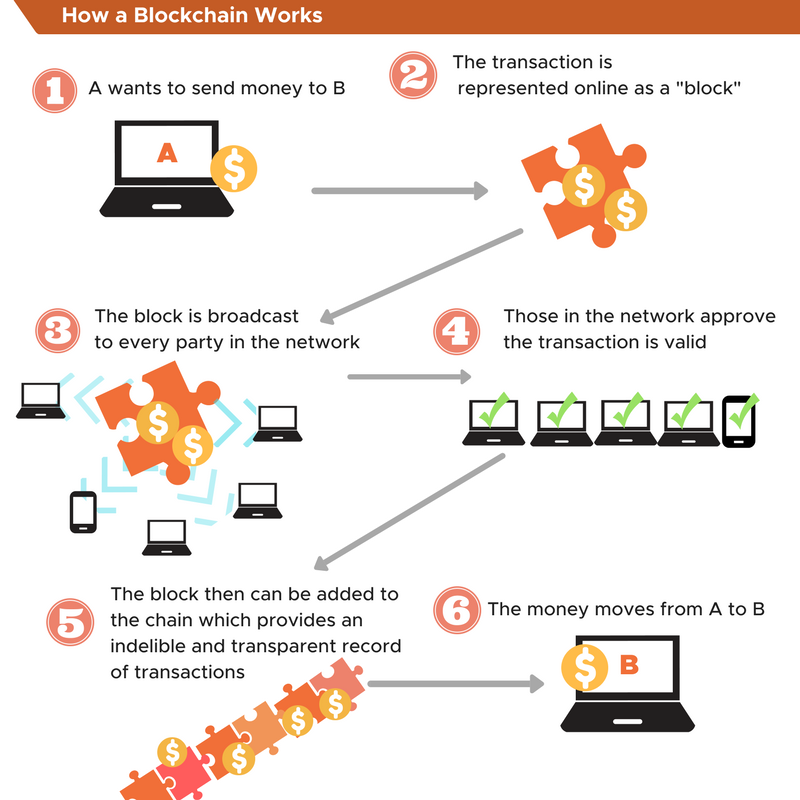
Diagram: How the Blockchain Works
Source: WeForum.org
You can also think of blockchain as a public ledger, but one that everyone can see and is shared amongst all its users. All the people using the blockchain keep the ledger up to date. It’s stored in a chain-like configuration, where the transaction history is stored in ‘blocks’ and can only be built upon, not changed.
To change the history – say, if someone were trying to hack it – the ledger would have to be changed in the majority of participants. With the number of people already using it, that’s near impossible. Imagine how secure it’ll be when there’s a mass uptake of it.
By having this digital ledger recorded on everyone’s computer around the world, it becomes decentralized. This is unlike a bank, where transactions are stored privately and are managed only by the bank. Blockchain is outside of any bank or government, which means there’s no central authority setting regulations on it. So you can say goodbye to the middleman who takes a fee (i.e. banks or other financial institutions).
The Advantages of Blockchain
In a report for the World Government Summit, ConsenSys gives a comprehensive summary of the main advantages of blockchain:
- Blockchain has no center, meaning everything is the same (it’s decentralized)
- Transactions are protected by the unchangeable nature of the ledger, offering greater cybersecurity
- Nobody owns or is in charge of the blockchain as a whole
If you want to learn more about blockchain today, check out the Growth Everywhere interview with the creator of online blockchain learning platform Blockgeeks.
There are many ways that blockchain is used by smart and innovative companies, but the very first one – and the one you’ve probably heard of most – is Bitcoin. This is where cryptocurrencies come in, but first, let’s talk about using blockchain for digital marketing.