A Change to Nofollow
Last month Google announced they were going to change how they treated nofollow, moving it from a directive toward a hint. As part of that they also announced the release of parallel attributes rel=”sponsored” for sponsored links & rel=”ugc” for user generated content in areas like forums & blog comments.
Why not completely ignore such links, as had been the case with nofollow? Links contain valuable information that can help us improve search, such as how the words within links describe content they point at. Looking at all the links we encounter can also help us better understand unnatural linking patterns. By shifting to a hint model, we no longer lose this important information, while still allowing site owners to indicate that some links shouldn’t be given the weight of a first-party endorsement.
In many emerging markets the mobile web is effectively the entire web. Few people create HTML links on the mobile web outside of on social networks where links are typically nofollow by default. This reduces the potential signal available to either tracking what people do directly and/or shifting how the nofollow attribute is treated.
Google shifting how nofollow is treated is a blanket admission that Penguin & other elements of “the war on links” were perhaps a bit too effective and have started to take valuable signals away from Google.
Google has suggested the shift in how nofollow is treated will not lead to any additional blog comment spam. When they announced nofollow they suggested it would lower blog comment spam. Blog comment spam remains a growth market long after the gravity of the web has shifted away from blogs onto social networks.
Changing how nofollow is treated only makes any sort of external link analysis that much harder. Those who specialize in link audits (yuck!) have historically ignored nofollow links, but now that is one more set of things to look through. And the good news for professional link auditors is that increases the effective cost they can charge clients for the service.
Some nefarious types will notice when competitors get penalized & then fire up Xrummer to help promote the penalized site, ensuring that the link auditor bankrupts the competing business even faster than Google.
Links, Engagement, or Something Else…
When Google was launched they didn’t own Chrome or Android. They were not yet pervasively spying on billions of people:
If, like most people, you thought Google stopped tracking your location once you turned off Location History in your account settings, you were wrong. According to an AP investigation published Monday, even if you disable Location History, the search giant still tracks you every time you open Google Maps, get certain automatic weather updates, or search for things in your browser.
Thus Google had to rely on external signals as their primary ranking factor:
The reason that PageRank is interesting is that there are many cases where simple citation counting does not correspond to our common sense notion of importance. For example, if a web page has a link on the Yahoo home page, it may be just one link but it is a very important one. This page should be ranked higher than many pages with more links but from obscure places. PageRank is an attempt to see how good an approximation to “importance” can be obtained just from the link structure. … The denition of PageRank above has another intuitive basis in random walks on graphs. The simplied version corresponds to the standing probability distribution of a random walk on the graph of the Web. Intuitively, this can be thought of as modeling the behavior of a “random surfer”.
Google’s reliance on links turned links into a commodity, which led to all sorts of fearmongering, manual penalties, nofollow and the Penguin update.
As Google collected more usage data those who overly focused on links often ended up scoring an own goal, creating sites which would not rank.
Google no longer invests heavily in fearmongering because it is no longer needed. Search is so complex most people can’t figure it out.
Many SEOs have reduced their link building efforts as Google dialed up weighting on user engagement metrics, though it appears the tide may now be heading in the other direction. Some sites which had decent engagement metrics but little in the way of link building slid on the update late last month.
As much as Google desires relevancy in the short term, they also prefer a system complex enough to external onlookers that reverse engineering feels impossible. If they discourage investment in SEO they increase AdWords growth while gaining greater control over algorithmic relevancy.
Google will soon collect even more usage data by routing Chrome users through their DNS service: “Google isn’t actually forcing Chrome users to only use Google’s DNS service, and so it is not centralizing the data. Google is instead configuring Chrome to use DoH connections by default if a user’s DNS service supports it.”
If traffic is routed through Google that is akin to them hosting the page in terms of being able to track many aspects of user behavior. It is akin to AMP or YouTube in terms of being able to track users and normalize relative engagement metrics.
Once Google is hosting the end-to-end user experience they can create a near infinite number of ranking signals given their advancement in computing power: “We developed a new 54-qubit processor, named “Sycamore”, that is comprised of fast, high-fidelity quantum logic gates, in order to perform the benchmark testing. Our machine performed the target computation in 200 seconds, and from measurements in our experiment we determined that it would take the world’s fastest supercomputer 10,000 years to produce a similar output.”
Relying on “one simple trick to…” sorts of approaches are frequently going to come up empty.
EMDs Kicked Once Again
I was one of the early promoters of exact match domains when the broader industry did not believe in them. I was also quick to mention when I felt the algorithms had moved in the other direction.
Google’s mobile layout, which they are now testing on desktop computers as well, replaces green domain names with gray words which are easy to miss. And the favicon icons sort of make the organic results look like ads. Any boost a domain name like CreditCards.ext might have garnered in the past due to matching the keyword has certainly gone away with this new layout that further depreciates the impact of exact-match domain names.
At one point in time CreditCards.com was viewed as a consumer destination. It is now viewed … below the fold.
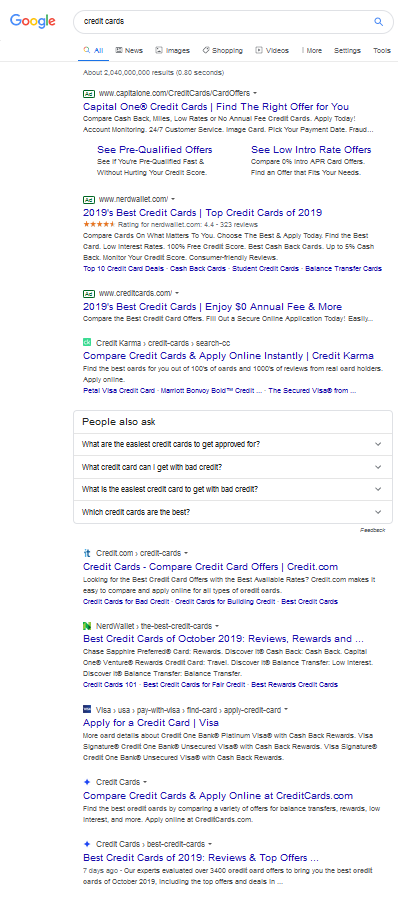
If you have a memorable brand-oriented domain name the favicon can help offset the above impact somewhat, but matching keywords is becoming a much more precarious approach to sustaining rankings as the weight on brand awareness, user engagement & authority increase relative to the weight on anchor text.
