Google Analytics periodically rolls out new tracking code. To date, the updates have supported:
- Improved data collection methods, such as asynchronous tracking, which was included in a 2009 update. The “ga.js” tag could be placed at the top of all pages. It improved not only tracking but also load speed.
- Enhanced data collection, such as Universal Analytics, which was rolled out in 2013. The “analytics.js” tag supported cross-device tracking, advanced segments, and custom dimensions and metrics.
- Multiple products in Google Marketing Platform, such as the Global Site Tag — “gtag.js” — which represents the most recent tag. Global Site Tag was launched in 2017.
The updates present a challenge to ensure the latest tags are installed. They also present an opportunity: getting robust data and reports that help drive your business.
Google Tag Manager
I addressed the basics of Google Tag Manager in “Getting Started with Google Tag Manager, for Ecommerce.”
Google Tag Manager can serve up the latest versions of Google Analytics’ tags. In many cases, Tag Manager automatically updates those tags.
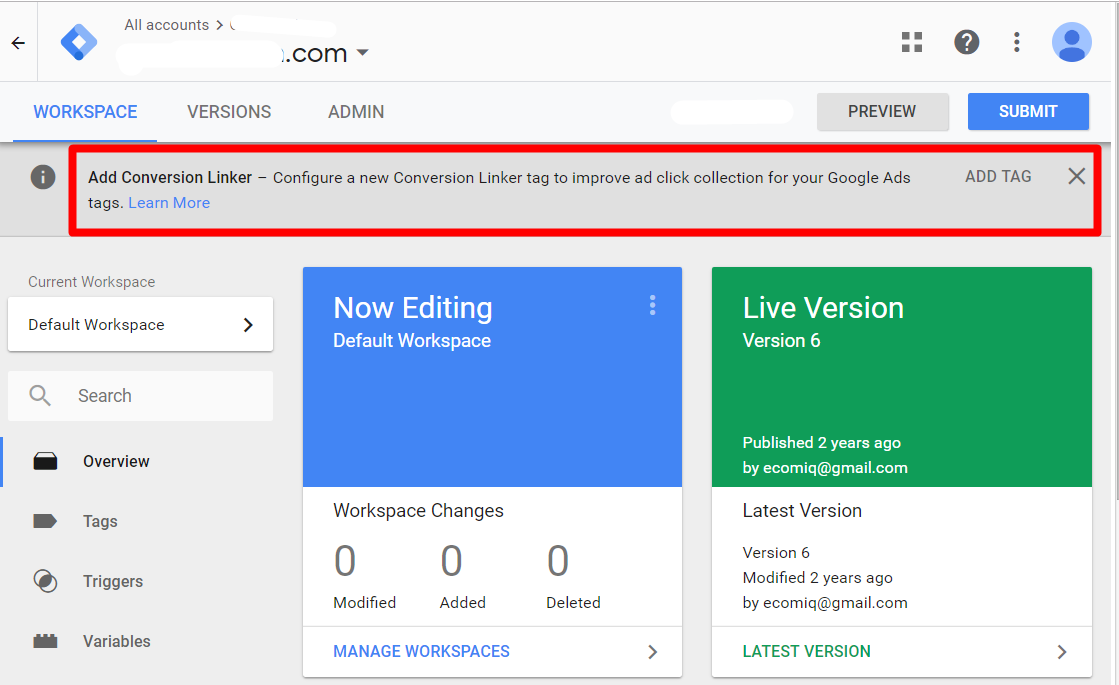
For example, Analytics recently introduced the Conversion Linker tag for Google Tag Manager. The tag addressed issues with Safari in tracking Google Ads (formerly AdWords) conversions. Since most online merchants use Google Ads and since Safari currently has about 15 percent share of the browser market, this update was essential to ensure conversions from Google Ads were properly reported in Analytics.
Updating Google Tag Manager for the Conversion Linker tag was fast and easy. But websites not using Google Tag Manager had to install the Conversion Linker code by hand, on all pages.
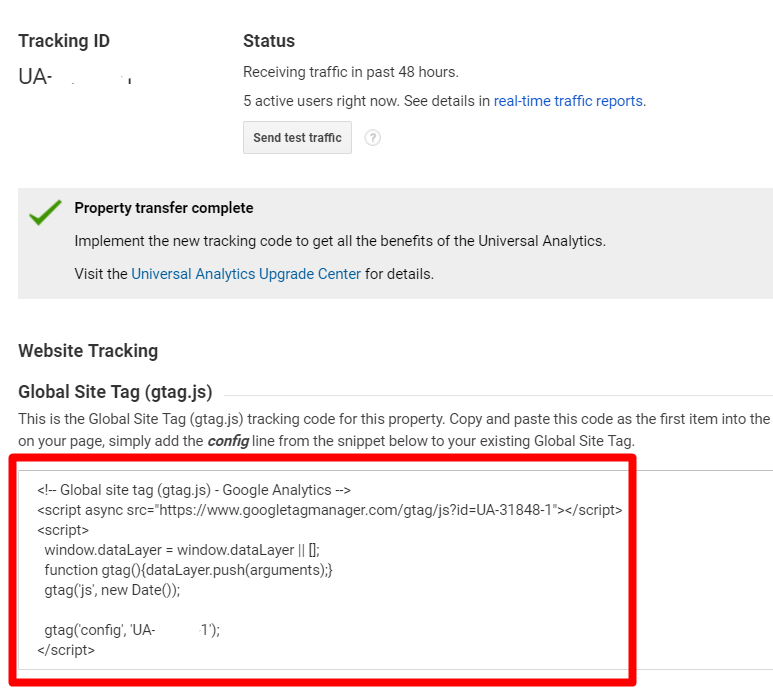
Global Site Tag
To determine the most current Google Analytics’ tag, click the “Admin” icon in the bottom-left of the Google Analytics’ user interface. Then, under the “Property” column, navigate to Tracking Info > Tracking Code.
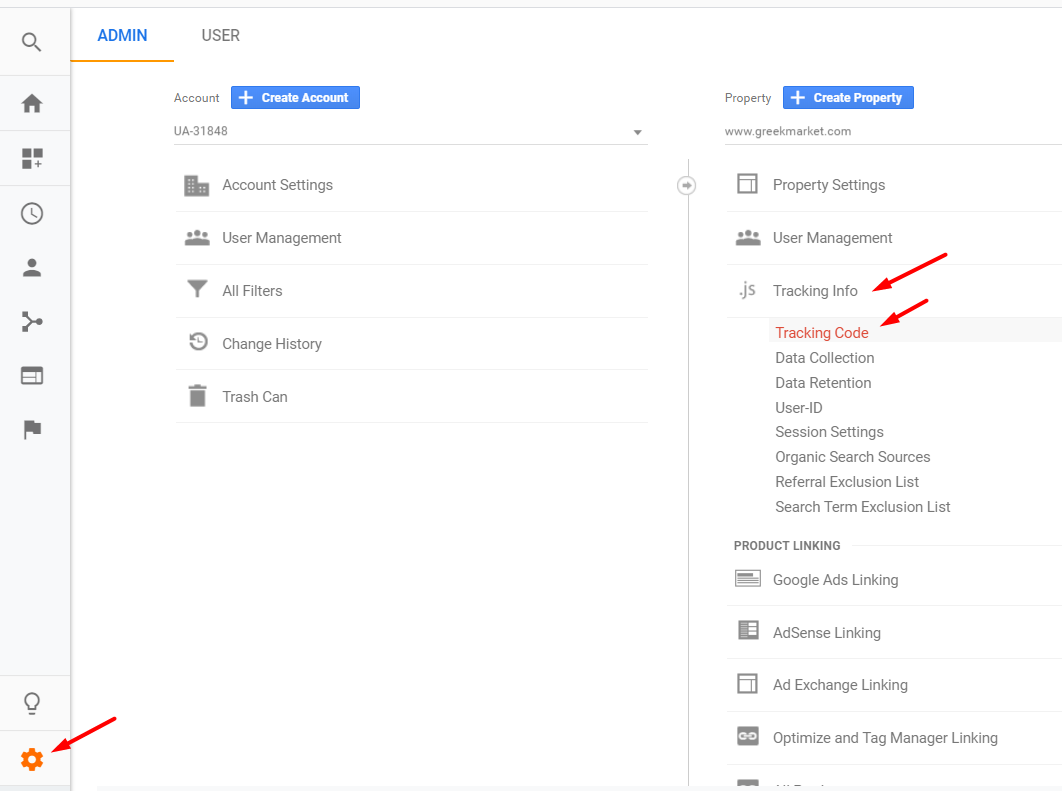
To find the most current tag, click the “Admin” icon. Then go Property > Tracking Info > Tracking Code. Click image to enlarge.
—
Compare the current code, as shown in “Tracking Code” above, to the code on your site. If the code is outdated, update it to what Google provides in the Admin settings.
—
Google typically notifies Tag Manager users for tag updates, as the example below shows.
Auditing Google Analytics
In addition to using the most up-to-date tags, always confirm that Google Analytics’ reports are accurate. I’ve addressed the general areas of concern, in my experience, at “How to Audit Google Analytics Data, for Ecommerce.” I’ve also reviewed potential reporting errors from Google Ads’ traffic at “Use Google Analytics to Audit PPC Traffic.”