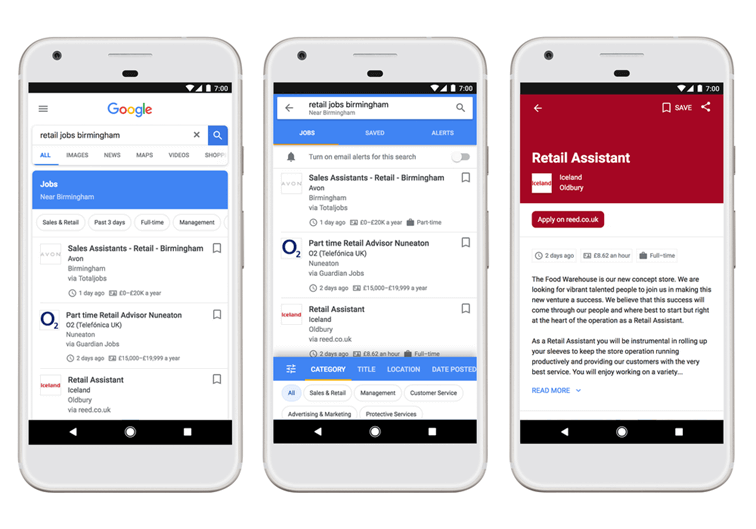
Looking for a new job can be a stressful experience. Even taking away the emotional part of the process, browsing job ads on companies’ websites, apps and job boards can prove to be mentally draining and time-consuming. Google, well aware of these difficulties, decided to find a solution to improve the whole recruiting experience. In May 2017, at Google’s developer conference I/O, Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai gave a sneak peek of it and released its official name: “Google for Jobs.”
Google for Jobs launch
Creating a candidate-first experience was a key requirement for Google, which decided to officially launch Google for Jobs in the US in June 2017. Through this product, job seekers were able to get exactly what they expected: exhaustive information about job roles, a high grade of consistency among vacancies and the ability to find a great variety of job offers, all in the same place.
On the other side, Google also wanted to provide easier discoverability for employers, providing in-house SEOs with a silver bullet: the chance to rank organically with job ads in the fiercely competitive recruiting market.
Why is this important?
Recruitment costs such as posting on job boards represent a huge burden for companies and in-house recruiters. This means that if a company is already facing a talent shortage or is suffering from high turnover, even a basic recruitment cost like posting job offers can spike to hundreds of thousands of dollars every year.
Once I heard about Google for Jobs rolling out internationally, I realized that this could have been a great opportunity for my clients. At that time, I was already optimizing the recruitment website for a large UK organization, so I immediately started pitching for the idea. Once approved, I started working on the Google for Jobs optimization, which can be summed up in these three steps:
1. Google for Jobs set up
Appearing in the Google for Jobs feature can be tricky at first, but the kind of exposure you could reach is immense, so my first recommendation is to have a good read of the Google Job Posting guidelines. Below, are a couple of key-points to bear in mind as well:
JobPosting schema markup
The first step to making sure the job posting pages are Google for Jobs friendly is to add the JobPosting schema markup. About this, it’s important to add the markup onto just the job ads pages, as content or pages with multiple listers will be ignored by Google. Regarding the structured data format, it’s advisable to use Google’s favorite JSON-LD, rather than Microdata. To create the code, I recommend using the Merkle Schema Markup Generator (see image below).
Through the tool, it’s also possible to access Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool and Google’s Rich Results Test (see image below) – both really useful in creating and validating the JobPosting markup.
Indexing API vs. sitemap
As job posts come and go quickly, in June 2018 Google also released a little gem called Indexing API. The tool, which has been created to specifically index/deindex Job posting and live stream pages, represents a step forward in making this particular kind of pages available to users just when they need it. Opposite to XML sitemaps – which are still recommended by Google for the entire site coverage – the Google Indexing API also represents a glimpse in the future for crawling and indexation, as the speed observed by Googlebots hitting pages are within 5-10 minutes. To complete the picture, I also recommend having a read of this clever Indexing API experiment by Tobias Williams, which demonstrated how the Indexing API triggered Googlebots to hit normal (non-JobPosting or live stream) pages within minutes, suggesting that Google lets you use the API freely, but without providing you any benefit to the SERP yet.
2. How to rank in Google for Jobs
Google for Jobs ranking factors are related to the completeness of the job posting details, including an exhaustive role description, an accurate salary bracket and an exact job location. For more details about how to improve the visibility, here are a few recommendations:
Job post content
Get the content of the job post right and you are halfway there. Here’s what to do and avoid:
Do:
- Add concise bullet points as they make the content easier to scan.
- Add the location (e.g. “North London”) straight to the copy, as this will improve the job post visibility if the users are looking for job + location queries, such as “JavaScript developer North London.”
- Create a simple, engaging piece of content. The copy should be easy to scan and have the following structure:
- Brief company intro
- Role description
- Key responsibilities
- Skills and experience
- Nice to have / desirable skills (optional)
- Working hours, salary and benefits
- Company information
Avoid:
- Avoid special characters, exclamations marks and capitalization.
- Avoid posting any job ad with less than 150/200 words. For competitive industries, increase this figure to 400/500 words.
Job post title
Job titles should be easy to understand and straight to the point. Here is what to do and avoid:
Do:
- Be concise, descriptive and use the role as a job title, such as: “Head of Sales & Marketing.”
Avoid:
- Acronyms, as a job title with just an acronym, will likely perform well just for acronym-related queries. For example, use “Vice President” instead of “VP.”
- Avoid references to the job location and salary in the title, such as: “Senior Java / Messaging Developer, London £100k”. This is because this strategy might let you to rank well for specific queries (i.e. “Java developer jobs 100k in London”), but score you low for broader queries.
Exact location
Adding the exact location (down to street and zip code) is another key factor in ranking well in Google for Jobs. As per the local results, the closer the user’s IP to the exact job post location, the better the chances to appear in Google for Jobs the vacancy has. Google also thought about remote jobs too. If you’re looking to recruit remote workers, simply add “jobLocationType”: “TELECOMMUTE” to the schema markup.
Job post publishing date
Particularly for competitive industries, it’s easy to spot a correlation between the job post publishing date and its ability to rank higher in Google for Jobs. The reason? Especially for industries with a high turnover like hospitality or retail, the ability to quickly fill vacancies is a crucial point for recruiters and job seekers. Regarding this, it’s also noticeable that most of job boards have a “validThrough” attribute set to 30 days from the publishing date, suggesting that freshness can definitely be considered as one of the Google for Jobs ranking factors.
Salary
In an optic of full transparency, Google also recommends to always display an accurate salary bracket. Regarding this, be also mindful about the fact that Google often compares the job ads with the industry average (see image below), clearly showing if you’re above/below what the market usually pays.
Employment type
It’s also best practice to add the employment type to the JobPosting markup, as this will trigger the employment type badge visible below. On top of that, please note that if you’re looking to display a vacancy available both as part-time or full-time you’ll need to create two separate job ads.
Expired job listings
Finally, it’s also worth mentioning that you should take extra care to let Google know when a job ad is expired, as Google is now threatening manual penalties about expired job ads, as explained in this note about how to remove a job posting.
3. Google for Jobs monitoring and reporting
The beauty of Google for Jobs is also that each impression, click and indexation issue can be easily tracked. This means that tasks like debugging, reporting and improving the job ads visibility are easier than ever, making the Google for Jobs a truly SEO-friendly search feature. Below are a few reports I recommend familiarizing yourself with:
Google Search Console – Enhancements
In order to appear in Google for Jobs, first thing to ace is to appear as a rich result. To do so, Google made available the below indexation/issues report that shows errors, warnings and validated pages.
In my experience, at the beginning it’s normal to expect a considerable amount of errors but get the schema markup right and the number of errors will drop to zero in no time. Regarding the warnings, these are recommendations that something on the markup is misplaced or missing, helping to make the code as friendly as possible.
To access this report, go to: Enhancements > Job Postings
Google Search Console – Job listings / job details
Another couple of Search Console reports are available from Search Appearance, too. “Job Listings” (1) is recording the hits each time a job post appears in the listings preview, whereas “Job Details” (2) refers to the impressions/clicks triggered by a specific job ad. On top of that, it’s useful to know that you can access the same data through the Google Search Console API.
To access this report, go to: Performance > Filter: Search Appearance > Job Listing / Job Details
Google Analytics – Traffic and performance
Google Analytics is another great tool to monitor the Google for Jobs performance. As Google automatically adds custom UTM parameters to each Job Posting, you can create a Google for Jobs segment in GA, effectively tracking traffic, applications and other key metrics.
To access this report, go to: Acquisition > All Traffic > Source/Medium > Search: google_jobs_apply
Also, don’t forget that from the same Analytics report you can also drill down by job role.
To access this report, go to: Secondary dimension > Landing Page
Google Data Studio – Dashboard
Another fancy way to report is through Google Data Studio, which gives you the ability to create any type of customizable dashboards. Apart from providing great visuals, I recommend using this tool for its ability to make data reporting easy and efficient, boosting collaboration.
Wrapping up
For the first time, job hunters can access a great variety of vacancies through an AI-powered dedicated search engine, helping them make more educated choices about their professional lives. At the same time, both small and big businesses have now a passport for reaching a large audience without incurring in any expense. So, why not make the most of this, and start experimenting with Google for Jobs right now?
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.