Reading Time: 5 minutesWhat is Google For Jobs?
Google for Jobs is a job search feature powered by Google that was launched in June 2017. For job applicants, it is a one-stop shop in a native user interface. It helps applicants save time without having to sort through a number of third-party job sites.
One job search can easily be tailored by location, title, date posted, company, and more. There is no special URL for the Google job search tool. Rather, job-seekers simply enter a query — such as “jobs near me” or “SEO jobs” inside the regular Google search box. Google will then add this Google for Jobs box into the search results.
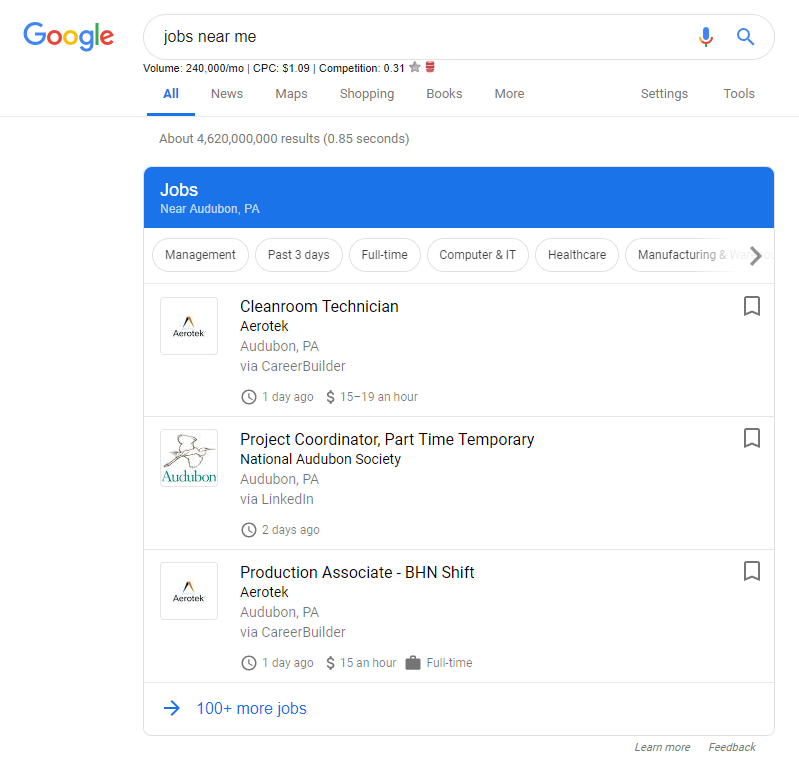
Once an applicant finds a listing that interests them, they will still have to go through an application process. (Google for Jobs is more of a vehicle to get the job seeker into a resume submission engine.) Many jobs also offer ratings and reviews of the employer from trusted job sites. Salary-range estimates are pulled from sites like Glassdoor and PayScale.
Advantages for Employer’s using Google Job Posting:
- For starters, it’s a chance to get great visibility on Google. Your postings are available to be displayed in the dedicated Job Search UI, featuring your logo, reviews, ratings, and job specifications.
- The new user experience allows job-seekers to filter by different criteria like location or job title, meaning you’re more likely to entice applicants who are looking exactly for that role.
Disadvantages for Employer’s using Google Job Posting:
- You can’t post directly to Google for Jobs, it is not an open job board; it’s a search tool that scrapes and highlights job postings that are already advertised. The easiest way to get job postings into Google is to mark them up using structured data, so some technical knowledge is required.
- If your website relies on direct traffic from “job wanted” queries, you may find this feature as an obstacle. Much like how rich answers sometimes deter clicks to publisher websites.
- The Google for Jobs platform seems to be a bit buggy on occasion. We observed some valid queries suddenly stop showing results for some unknown reason.
- According to this website, you may run the risk of being penalized if your closed jobs are shown as open. This is likely to defend against spam.
Posting Your Jobs on Google:
More information can be found on Google Developers.
Google For Jobs, at this time, seems to favor the third party websites (Simply Hired, Linkedin, Glassdoor, Indeed, and the many others out there). However, we have seen the occasional direct link to a company’s direct careers portal.
For the former, Google seems to have already figured out how to read and extract the information from the third party sites. For the latter, you will need to add job listing structured data to your careers page. The structured data allows Google to pull in specific fields, such as the job category, location, company, salary, and more (more on this below). Unfortunately, this seems to be where Google For Jobs is still maturing. For this post, we tried to get our own Greenlane career page to rank in Google For Jobs, to no avail.
Recommended for You
Webcast, March 26th: Winning Lifecycle Marketing Strategies for 2019
It seems to be a product Google is still focused on. In the Google Search Console, you will be able to see the number of clicks, CTR, and position for your job postings. So that’s a sign that this isn’t an experimental product.
Here are just some of the ways you can increase your job post’s Google ranking

- Get detailed when describing skills, responsibilities, and qualifications: People will often quickly skim through a job search when looking for openings. This means your job description needs to be sharp, concise and well executed. But when you create your listing for, say, a Social Media Manager, Google is going to expect to see words in your job listing that show up in other Social Media Manager listings. Because Google has examined millions of other Social Media Manager job listings, they’ve picked up on a semantic connection between words like “social” and “ads.” When connecting words like these are found together, they provide more context for Google. Search algorithms then, having a greater knowledge of a listing, can rank it higher for relevant words. Google considers the semantic relation between words and keyword density to determine relevance for their main search engine; so it’s likely this is a factor here.
- Choose a standard job title that’s likely to match searches made by job-seekers.
- Advertise a specific salary: For the best chance of appearing higher on Google searches, you should always display an accurate salary bracket. (This is one item Google seems to require, even though some hiring companies would prefer not to publish it).
- State the exact location. Displaying an exact location of the job, including zip code, will increase your job’s chances of being seen.
Your job postings should have schema markup
For the best chances to show up in Google for Jobs, and possibly rank higher, you have to provide a list of schema properties in your HTML code. Below are two tables: one for the required properties and one for recommended properties. We recommend providing both types of properties to maximize your job’s SEO potential.
Required Schema.org Properties for your Job Postings:


If you have an HTML/CSS expert in-house, they can help you apply Schema markup to all your job pages.
A Note About Third-Party Job Boards
As noted above, Google for Jobs is pleased to republish job listings from ZipRecruiter, Monster, CareerBuilder, LinkedIn, etc. They’re also pleased to send them traffic through this platform. But, Google knows that if they sequentially own the relationship with job-seekers then they’re really the ones that own the job market.
Google for Jobs earns its profits from job-seekers. The more Google keeps their users on their job search platform, the more likely they are to click a paid ad. Therefore, Google has developed a job search platform that quietly but strategically works in their favor.