Modern businesses need to “run on all cylinders” online. That usually entails maintaining social profiles, building a website, and other activities. It also entails managing reviews. Not only does that mean responding to reviews and striving to receive positive reviews, it also means using those reviews on websites to improve conversion rates and enhance SEO. In this article, we’ll talk about different ways to do that and we’ll discuss some review use cases explaining the possible results.
Why Customer Reviews Are Important to Businesses
Positive reviews increase the perceived trustworthiness of a business or brand. A survey conducted by Moz found that 67.7% of purchase decisions are affected by reviews. One benefit of having reviews is that, if they’re positive in relation to those of competitors, the business gains market share and increases sales. It’s also very likely that the business or product will be displayed more frequently in search results on search engines and retail websites. But getting lots of positive reviews shouldn’t be the extent of a business’s reviews strategy.
Once a consumer chooses a product, service or supplier, there’s still a chance he won’t follow through with a conversion. Strategically placed and curated reviews can improve the traffic flow to shopping carts, lead forms, and confirmation pages. Review content, a kind of “user-generated content” or “UGC,” provides SEO benefits as well. We’ll discuss some easy and effective ways to select and organize reviews and get better marketing performance in the following sections.
Using Reviews to Improve Conversion Rate (for Conversion Rate Optimization)
Simply put, CRO aims to increase the flow of traffic through a marketing funnel. It has the effect of increasing sales and improving return on ad spend. For more information about the importance of CRO, see our article What is Conversion Rate Optimization Anyway? For those of you who are already up to speed about CRO’s purpose, this article will explain the importance of customer reviews in CRO strategies. There’s a strong case to support the argument that reviews and similar forms of “social proof” are one of the most important aspects of CRO.
As we explained above, consumers pay attention to reviews when they’re making decisions and building relationships with brands. Positive reviews drive sales, especially when they’re more positive than competitors’ reviews. That’s why businesses try their best to gather as many positive reviews as possible. You can see here that the “best seller” desktop speaker on Amazon has a strong average review score (about 4.25 out of 5) and over 4,000 reviews. The next product has a great average score as well, which is one reason Amazon displays the two products near the top of the list.

What about when the consumer has already chosen a seller or is investigating a seller’s product in detail? Let’s say a competitor has a clear edge with lots of great reviews and a 5-star score on Amazon. Even if that’s the case, a competing product has the potential to stand out in other ways. Maybe it has unique features or is being sold by a more established brand. A shopper might click on its listing to investigate it further. In some cases, a seller can attract traffic directly to his website, bypassing the “marketplace” of competitors on Amazon, walmart.com, etc.
This is when reviews are the most useful; right on the product or service page of a business’s website. There, the seller can choose relevant, persuasive reviews to seal the deal and increase conversion rate. There, the “noise” from competitors and third-party sites is no longer present and the page can be optimized for best results. It’s one of the last steps before a transaction may be completed. Often, advertising money will have been spent to bring a consumer to this point. It’s important to sell here. User-generated content is a powerful persuasive element that drives more conversions. There are many kinds of UGC. Examples are photos, videos, and comments. These can be gathered from reviews, from social media, or even from other sources. Try using multiple kinds of content together to find out which combination improves conversion rate the most.
Most landing page CRO guides and checklists suggest placing testimonials, reviews, “star ratings,” (i.e. average scores out of 5 max), or another form of social proof near the pitch or product description. Thought leaders contributing these suggestions include Unbounce, Hubspot, and Klientboost.
In practice, there’s plenty of data supporting the idea. Here are some review use cases.
- Esurance increased conversion rate by 11.5% by adding testimonials and star ratings to their site. (Source)
- Express Watches increased conversions 58.29% by placing reviews and average ratings on product pages. (Source)
- A test by Unbounce compared performance with testimonials towards the bottom of the page versus the same testimonials being higher up on the page. Conversion rate increased 64%! (Source)

The image above shows user-generated reviews and photos at balanceathletica.com. Notice the company’s response to the comment at the bottom-right.
The great thing about user-generated reviews is the endless supply of content available from genuine sources (i.e. customers). The more reviews that are available, the more a business can use to test and maximize the conversion rate. A/B testing reviews is a great way to do that. Useful apps like StackTome allow CROs to test different reviews and find out what context, sentiment, and recency of reviews impacts conversion rate the most. We elaborate on this below. Keep reading.
SEO Benefits of Reviews
Let’s talk about search engines and site traffic. Businesses get more impressions on SERPs when they have lots of reviews, especially if they’re mostly positive reviews. OptInMonster puts reviews in the top 10 most important overall SEO ranking factors. Frequent reviews help out a lot, but don’t get fake reviews. Search engines will index them and you’ll be penalized with fewer SERP listings. Reviews on Yelp, Google, Facebook and other sites all help. It’s also worthwhile to use some semantic tags for reviews so that search engines can more easily recognize and utilize them. Here’s how you can use schema markups to do that.
In the example below, Google determined that local listings would be most helpful for the “kitchen supplies” search query. It’s clear that the geographic proximity of these stores was prioritized heavily in this case (we searched from Cary, North Carolina, US), but it’s also clear that the quantity of reviews and their high scores was another high-priority factor. Local SEO certainly benefits from reviews just as non-local does.

Reviews increase SERP surface area and eye-catching factor as well. See below how the first listing is slightly larger and more colorful than the second, thanks to its review score.

Now let’s take a look at how search engines utilize web page content and why reviews are excellent content to have. Ideal content is filled with exact and semantically related keywords that give search engines context to help determine when a page should be listed on a SERP (search engine results page). Reviews are naturally filled with these keywords, which is why they are excellent SEO site content.
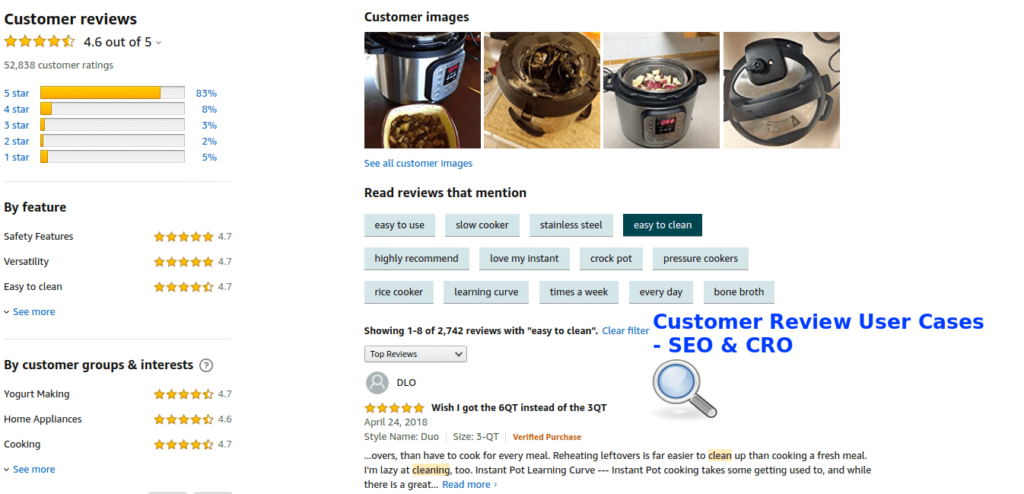
Exact keywords are, of course, an exact match. For example, a product is called an “leather shoe conditioner” and that is exactly what the search was for. Semantic keywords relate to the product in various ways and help to give search engines context. Keywords like “leather care,” “leather boots,” and “repair scratches in leather” are all related to the leather conditioner product and help the product page show up for more searchers even though they don’t describe the exact product. It’s recommended to use a few kinds of semantic keywords, as digital marketing expert Neil Patel explains here. Usually it takes lots of research to find these keywords, but reviews provide a stream of potentially useful ones that are verifiably related to corresponding products. Below you can see how Amazon categorizes reviews by things mentioned in them. Most of the examples of things mentioned here could be useful as semantic keywords on a product page for the pants in the photo.

Besides including exact and semantic keywords on pages, refreshing the page content is another best practice that helps businesses gain more traffic. Reviews provide a convenient opportunity to update page content, especially if there are new reviews available regularly. This can be done automatically with a good reviews app, which we’ll discuss later.
Article was originally published here: Source Link