Search engines are now using data-driven factors to determine how relevant your website is to a particular search query
The practice of search engine optimization (SEO) has experienced monumental changes over the course of the last 15 years. When SEO first broke onto the scene, it was quickly discovered that webmasters could manipulate search results and make their websites rank well merely by packing their target keywords into the website as many times as possible – a practice known as “keyword stuffing”.
This majorly skewed and distorted Google’s and Bing’s search rankings, since low-quality, “spammy” websites were quickly able to outrank reputable and relevant websites. In response to this unfavourable outcome, these search engines rolled out several rounds of algorithm updates, permanently changing the way in which websites are ranked.
Presently, Google and Bing each use hundreds of different factors – with varying levels of importance – to rank websites, helping to ensure high-quality search results for their users.
So, while pursuing your target keywords and acquiring quality backlinks are still important, today, these are increasingly becoming a smaller part of the overall puzzle. Search engines are now using data-driven factors to determine how relevant your website is to a particular search query. These include such factors as the quality of your web interface, as measured by your user metrics, and this is where user experience (UX) comes into play.
What is User Experience (UX)?
User experience is the study of how users perceive and interact with a web interface. Its main purpose is creating a user-centered web experience, with a focus on “pain points” – points where the user is confused by the interface.
Effective UX design helps your users to find what they are looking for. It also helps engage your audience, and this has a positive effect on the various user metrics that Google and Bing employ in their search rankings. Focusing on creating engaging user experience will have a “trickle down” effect on your search ranking. When you make your audience happy, you make Google and Bing happy.
What Are the Most Important User Engagement Metrics?
There are many different metrics that we could discuss, here, but we’ll focus on those that have the most impact on your search ranking. These are the metrics that gauge how well your website engages your audience, as an indication of how relevant your website is to a specific search query.
1. Bounce Rate
Your website’s bounce rate is a metric that communicates the percentage of web users that exit your website after only viewing only one page – often this is either your homepage or a landing page. A high bounce rate can be an indication that your users did not find what they were searching for and left after visiting only the initial page.
Although there are many possible reasons for a high bounce rate, there are several causes that we see most often. These are poor web design, confusing UX design, irrelevant or poorly formatted content, and slow site speed – among other factors.
Since your bounce rate is correlated to the relevancy of your website, Google and Bing have heavily factored it into their search algorithms. You should take the necessary steps to ensure that you maintain a low bounce rate for your website.
2. Page Dwell Time
A second metric that search engines give consideration is the amount of time your users spend on the website – called “dwell time”. Search engines consider the amount of time users spend on a page as an indication of how engaged they were. Having high dwell time suggests that the content is interesting and relevant to your audience. The inverse is true of low dwell time. In both cases, your search ranking is adjusted accordingly.
One simple way to ensure high dwell time is to focus on creating insightful, relevant content, which will engage your audience and positively impact your user metrics.
UX Design Factors to Focus On
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork of which user metrics are relevant to SEO rankings, let’s discuss how we can improve those metrics by focusing on creating engaging UX design.
1. Load Time / Page Speed
There aren’t many things more annoying for web users than waiting for a slow website. With each second that passes, it becomes more and more likely that your audience will exit your website before it ever loads. Even though the page never loaded, this will still register negatively and increase your bounce rate.
Even though there’s a variety of possible culprits for slow site speed, only some of them are within your control. Even though you can’t control your user’s slow internet connection, you can make sure that your website is fully optimized to ensure the fastest loading time possible. This might mean minifying your file sizes, optimizing image sizes, and making sure your website is making the fewest possible server requests.
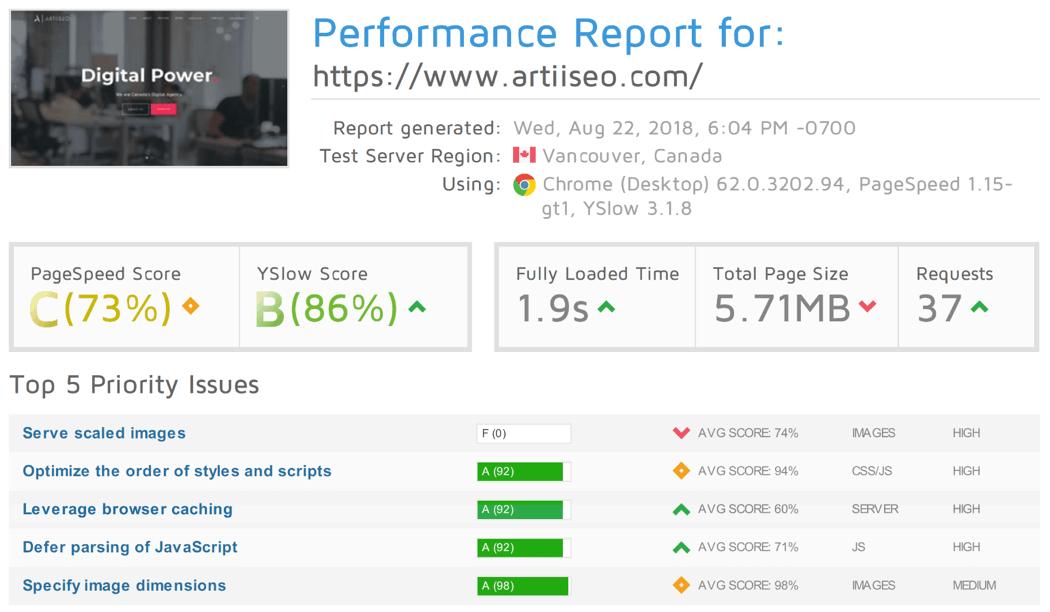
These, and others speed factors, all contribute to the overall speed of your website. Unfortunately, we do not have the space to cover this topic as comprehensively as we’d like, but you can read more about site speed from the blog. Below, is a snapshot of our website’s speed test results, performed with GTMetrics.
2. Mobile Responsiveness
With more than 50% of all web traffic now coming from mobile devices, mobile responsiveness has never been more important and is one of the primary aspects of effective user experience. If your website isn’t mobile responsive, you’re forfeiting more than 50% of your audience from the start. Google tests the mobile responsiveness of every website, using their Google Mobile Responsiveness Test and weights this factor heavily in their ranking algorithm. Websites that aren’t mobile responsive will see their user-engagement metrics plummet.
3. Implement a User-Friendly URL Structure
Implementing a user-friendly URL structure is an integral part of an effective user experience strategy. Effective URL structures help to orient the user in terms of where they are in the overall hierarchy of your website. They also help communicate what the page is about. Ineffective URL structures are exactly the opposite; they have no hierarchal structure and offer little to no insight about the contents of the page. The example, below, is an example of a poor URL structure:
- “https://www.chapters.indigo.ca/en-ca/books/product/9780771057717-item.html?s_campaign=Google_BookSearch_organic”
Care to guess what this website is about? Maybe, something to do with books? But even then, which books?
This URL structure is a prime example of an ineffective URL structure that confuses both web users and search engines about the contents of the page. Search engines use URLs to understand and index web pages and the keywords in your URL play an important role in your overall search ranking.
You should focus on crafting clean, coherent URLs that can be understood by both users and search engine crawlers. Implement URL structures that users and search engines can decipher. The example below shows an effective URL structure:
- “https://www.smartinsights.com/mobile-marketing/mobile-marketing-analytics/mobile-marketing-statistics/”
This four-tier URL has implemented an organized, efficient URL structure that is both understandable and displays website organization, with each subfolder containing a sub-topic of the previous broader topic category.
1. Headers & Menus
Headers, and more specifically, the menus you place in your headers, should be efficient and clean. I’m sure you’ve seen websites where the menu was so cluttered that you weren’t sure where to go. There was probably little to no categorization, and it seemed like every page on the entire website got a spot on the menu.
This isn’t effective user design.
As bad as this scenario sounds, it is a very common issue that we see on many websites. Your audience will feel confused and overwhelmed with the extent of content presented to them and may even exit the site rather than go on a ‘Columbus-esque’ quest to find what they were originally looking for.
2. Streamline Your Menus
Menus are one of the main features of any website, and their primary objective is to guide users to the proper page or section of the website. One of the primary tenets of effective UX design is streamlining the design and structure of your menu.
You’ll want to make sure that your menu isn’t overly cluttered or complex. It isn’t helpful to place too much content in your header or menu. Yes, you want to make sure that your audience can find what they’re looking for, but it’s better to accomplish this by creating effective categories and subcategories.
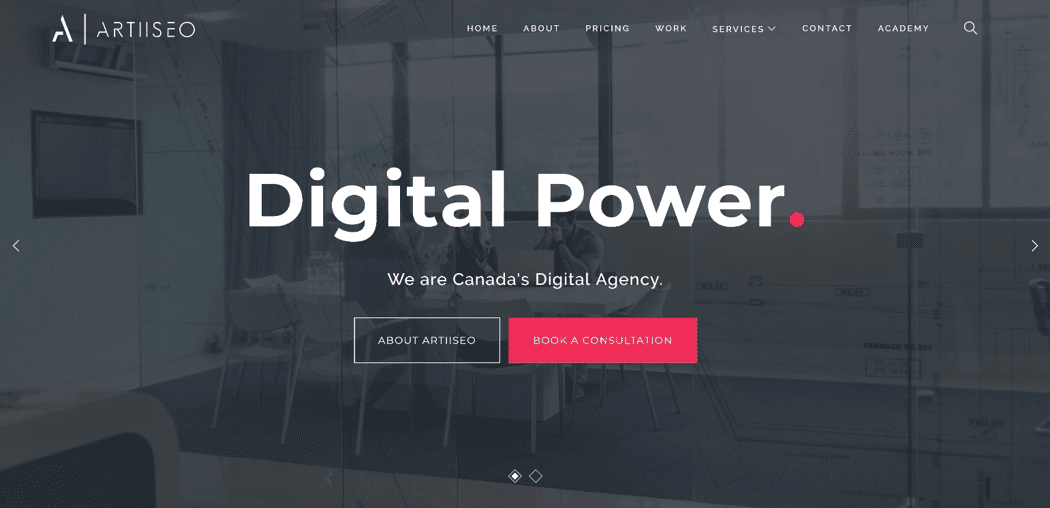
One example of this would be the menu on our website, below. It isn’t crowded, and any extra content or pages are placed in a drop-down menu.
Summary
In conclusion, user experience design should be a primary consideration of any SEO campaign. UX design has a direct and powerful impact on your SEO rankings through the various metrics that search engines use to track user engagement. It helps you understand how users engage and interact with your website, as it considers such factors as page speed, mobile responsiveness, menu/header layout, and URL structure.
Focusing on implementing effective UX design will dramatically boost your user engagement metrics, which will subsequently influence your overall search ranking.
