We’re entering a new era of optimizing for search engines.
And no, SEO is not dead.
While many things stay the same in search, we can’t deny the new path we’re on with the introduction of machine-learning systems like Google’s RankBrain.
The concept of RankBrain may seem technical and daunting, but it’s one that CMOs — not just technically savvy SEOs — must understand to be competitive in the months to come.
In this post I cover:
- What RankBrain is.
- How search results are changing.
- How to evolve your digital marketing strategy for machine learning search algorithms.
- And why you might need PPC advertising even more than ever.
An Intro to RankBrain
RankBrain is a machine-learning artificial intelligence system that came onto the scene in 2015.
Bloomberg was the first among mainstream media to break the news of RankBrain, Google’s newest addition to search rankings.
And while we officially met RankBrain in 2015, Google was talking about it as early as 2013.
RankBrain is designed to better understand the meaning behind a searcher’s words. This 2013 post at Google discusses this concept of understanding word relationships if you want to learn more.
From the Bloomberg article we learned that 15 percent of queries per day have never been seen by Google before. RankBrain helps interpret those novel queries.
At the heart of RankBrain is a goal to better interpret search queries and serve the most relevant search results. This has been a lifelong goal of Google Search.
We discuss this at greater length in our SEM Synergy podcast http://www.semsynergy.com/ (July 2016) here.
Mobile: A Primary Driver of RankBrain’s Existence
Mobile drove the need for RankBrain even further. Mobile search behavior has been a game-changer, especially when it comes to voice search, something a lot of mobile users take advantage of.
As you may know, queries tend to be much more conversational using voice search versus typing.
RankBrain deals well with the long-tail queries that are common to voice search today, though there are plenty of long-tail searches typed into a search bar, too.
I believe that RankBrain is preparing for a world where voice search will become more and more the norm.
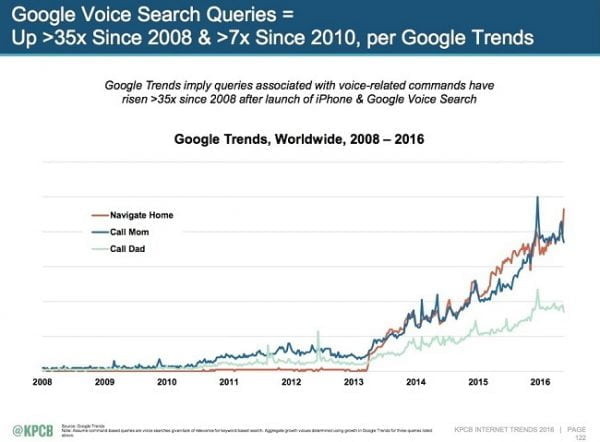
Remember, voice search is already on the rise. In a presentation by Mary Meeker on the popular 2016 internet trends report, we see that voice search is up 7x since 2010.
And it’s not just voice search coming from mobile devices. Now, we have to consider things like voice assistants such as Google Home, where it remains to be seen how the device’s answers will pull from web results.
Here’s What RankBrain Does
RankBrain was designed to better analyze the language of websites in Google’s index, and then apply that analysis to a search query. By better understanding the search query, it can better match users with websites and pages.
The purpose is to better understand the meaning of content and the intent behind a search query.
Once RankBrain better understands the intent, it can then presumably apply the appropriate Google algorithm signals that deserve the most weight for that query.
Along with being able to understand concepts on a web page better, RankBrain also allows for a better understanding of the association between multiple queries, like:
“Where is the Eiffel Tower?”
Followed by:
“How tall is it?”
How Does RankBrain Learn? Examples of RankBrain in Action
Essentially, RankBrain can take sets of “training” data created by humans to help establish a baseline, and then can apply machine learning to determine the best search results based on a variety of factors over time.
Google confirmed in the Bloomberg article and in this article at Search Engine Land that they periodically update the system by giving it new data to better reason with new concepts.
At SMX West 2016, some presenters shared examples of RankBrain in action.
One study showed how RankBrain better interpreted the relationships between words.
This could include the use of stop words in a search query (“the,” “without,” etc.) — words that were historically ignored by Google but are sometimes of critical importance to understanding the intent behind a query.
For example, take the television series “The Office.” It’s an example of a search that would be taken out of context without the all-important “the.”
Here’s another example query from an interview with Googler Gary Illyes: “Can you get 100% score on Super Mario without walk-through?” Ignoring “without” would potentially return search results on getting a 100 percent score on Super Mario with a walk-through … so the opposite of the results a person was trying to get.
There are other theories on how RankBrain might use data to learn what the best results are for a search query. It’s possible that searchers’ engagement with the search results may be a factor in how RankBrain determines the relevancy of a result, as Rand Fishkin posits in a keynote from July 2016.
For example, if someone clicks a search result and doesn’t go back to the search results to start clicking other web pages, this could indicate the searcher found what they were looking for.
The machine could then learn over time that a low bounce rate signals a relevant result, so that web page could show up more often and higher in search results.
Here’s a visual of that concept from Fishkin’s presentation:
How RankBrain Works with Other Ranking Signals
As I mentioned earlier, RankBrain is essentially built into the query process to better understand language and make an improved match between the search query and the websites in the Google index.
Remember that Google still has hundreds of other signals it can apply to a search query to identify the best results.
In 2016, however, Google confirmed that RankBrain was among its top 3 ranking signals for search. Rounding out the top 3 are content and links.
This is an important concept to understand. Google clearly stated that the signals that we’ve come to know to be important and that we’ve been optimizing for still matter: content and links.
While the content on a website and its links are both essential to determining meaning and relevance, RankBrain works in partnership by assisting the Google search engine to better determine if a website is the most relevant based on signals and algorithms, given the searcher’s intent.
The Impact of RankBrain on Big Brands
With machine learning, RankBrain learns associations over time. That means, if a brand becomes associated with a certain product, the queries about that product may lead to more branded search results.
Because Google tends to favor big brands online for a variety of reasons, with RankBrain things like the site’s engagement rate, mentions of the brand across many social sites and so on could further enhance favoritism here.
This could happen despite the fact that some bigger brands may have a weaker link profile than other websites in their space.
What RankBrain Means for Your SEO and Digital Marketing Strategy
OK, now for some action items …
SEO and Your Content
First, let’s talk content. For many, it’s actually business as usual.
Examine your content to ensure it provides the best, most complete answers to a query, whether you’re an informational page or selling a product.
RankBrain is a machine learning system, but it still needs input from your website.
Yes, it’s working to better make connections about concepts. For example, we can give RankBrain credit for understanding a page is about baseball even if the word is never used and only “Chicago Cubs” and “New York Yankees” are present on a page.
Absolutely one of the goals of SEO is to better help search engines understand what your content is about. It is still vital that you make sure you’re including the keywords that are important to your business on your website page.
This includes keyword “stemming” (like “walked” and “walking” along with “walk” and “walks”) and using synonyms and natural word variations to help make connections between ideas.
One example we use in our SEO training classes is the word “mercury.” You can use “mercury” 10 times on a page, but if you forget to use the word “planet,” then the search engine may be confused about the subject of the page. Is it an element, car, insurance or other?
This is also a time to explore structured data markup, which helps search engines better make connections as to what is on the page.
Remember, the little things matter as they always have in SEO.
You’ll want to continue to pay attention to making your search results listings stand out in the crowd. That means ensuring each web page has custom meta data in addition to exploring other ways you can make it stand out using schema markup and useful, engaging copy.
Another question to ask: Once people land on your website, is it helping them move farther along in their journey by offering up related content that explores a topic/product/service more?
This can be accomplished by siloing your content to create subject themes around the key terms that are important to your business.
Subject organization chart aka siloing
RankBrain and Digital Marketing Strategies
I mentioned earlier that RankBrain will likely favor big brands. So what happens if you’re not a big brand?
Now is the time to start thinking about how to supplement your digital marketing strategy, if you haven’t already.
While it’s a great idea to have a thorough SEO strategy, it’s never a great idea to put all your eggs into one basket.
So in the era of RankBrain, even though the basics of SEO that we know and love are still important, you’ll want to think of creative ways to grab that SERP real estate.
That means if you’re not in the upper echelon of brands online in your space, consider supplementing your search marketing strategy with pay-per-click ads.
RankBrain Is Not the End of SEO
If you’ve been concerned about how RankBrain impacts SEO, there’s possibly more to worry about than you may think.
RankBrain is search results relevance on steroids. Simply put, you must improve your content relevancy to match the query intent. Yes, SEO best practices are critical to traffic, and rankings are more competitive than ever.
But you must also focus on your content from a macro and micro level, and how your website’s content as a whole helps to answer the questions your audience is looking for.
And don’t forget to supplement your digital marketing strategy with things like paid search, social and other channels to keep your brand top of mind.
Do you have insights on the impact of RankBrain on search rankings? I want to know. Leave a comment below.
We can help with your RankBrain optimized SEO strategy. Our services are tailor-made to match your goals and audience. For more revenue through digital marketing, let’s talk.