Reaching the first page isn’t enough anymore, you need to place your business in the #1 position
Ranking higher among a congested competition in Google is a mandatory goal for many businesses today. If you are an e-commerce business, are you aware of the SEO tactics and requirements to take you to the top? After all, if you aren’t generating enough clicks, you’re not generating sales.
The following data should show you why a powerful SEO strategy for your e-commerce website is necessary.
Around 44% of online shoppers initiate their search through a search engine. According to the data provided by the US Department of Commerce, in 2015, the e-commerce sales per year reached $341.7 billion, which is a 14.6% increase from that of 2014s $298.3 billion. Furthermore, the data also stated that online shopping accounted for 7.3% of the total retail sales in 2015, as compared to 6.4% in 2014. Updated data for 2017 and 2018 is also available.
According to the 2017 data provided by Ignite Visibility, the links ranked on the first position in Google registered a click-through rate (CTR) of 20.5%, following a sharp decline of second-ranked with 13.32%, and third-ranked with a 13.14%.
Another study at Marketing Land backed the data provided by Optify by stating how the chunk of impressions coming from the first positioned website is almost twice that of the second position.
In short, reaching the first page isn’t enough anymore, you need to place your business in the first position.
Speaking in terms of repercussions, if you don’t have a sound SEO strategy, then your brand impressions, clicks, conversions and revenue will suffer.
Coming back to your e-commerce website, an effective SEO strategy requires a series of steps to take it to the top. As for this discussion, we will talk about the preliminary considerations of relevant researches to form the stage for your SEO campaign to stand on.
Research
It is imperative to start with research, prior to starting any on-site or off-site SEO work.
Undoubtedly, research is the most important tool in SEO, as targeting incorrect keywords can destroy your campaign by producing low-quality traffic and negligible conversions.
Keyword research
When conducting keyword research, there are three main areas you need to focus on.
1. Locate keywords for your homepage and product pages
When we talk about optimizing the most important pages of a website, it is crucial to consider the search volume, relevancy, and ranking difficulty.
Aim for keywords that are specifically relevant for your brand, display a high exact match search volume (local and not global) in Google’s free AdWords Keyword Tool and acquire a low difficulty score from Moz’s keyword tool.
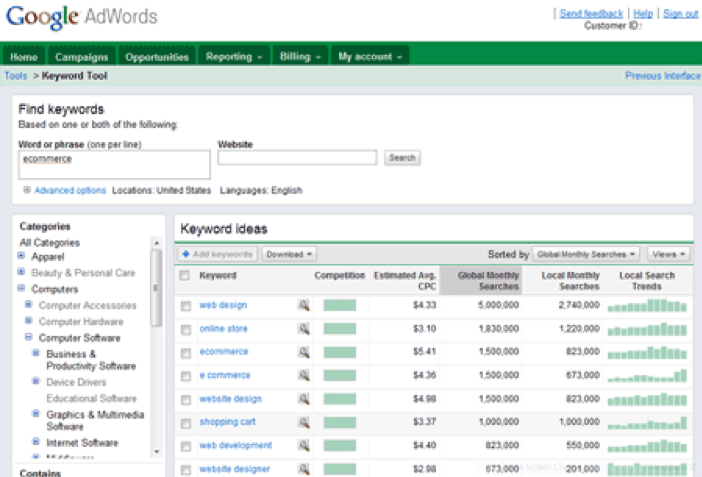
However, stay away from broad and highly competitive keywords. If the match is quite broad, there is a high chance of an increased bounce rate and low conversation rate because people are clicking through to your site, but unable to find their preferred content. In the case of keywords featured in a high competition, it will take eons to climb the rankings ladder.
Consider you’re the manufacturer of “all natural” tea filters. Here you won’t be targeting “tea”, “natural tea” or “organic tea”, as these keywords aren’t specific in nature for visitors interested in tea filters. Furthermore, those keywords are highly competitive and you will find it almost impossible to compete against an ocean of tea manufacturers.
2. Find keywords for blog topics
Creating a blog is a great exercise for e-commerce websites in order to uncover further keywords that might not have been featured on your homepage. Additionally, you can benefit from long-tail keywords within your blog.
The prospect of ranking “tea” might feel exciting if you sell tea leaves, however, data indicates that popular, generalized terms like “tea”, “coffee”, etc. capture less than 30% of the entire web searches. Hence, the need for long-tail keywords come into existence.
In other words, the remaining 70% chunk is captured by the long-tail search. The long-tail keywords are responsible for hundreds of millions of unique searches conducted a few times in any random day. According to Profitworks, long-tail keywords register conversions 2.5 times higher than the head keywords.
Therefore, going after long-tail keywords featuring high exact match search volume (local and not global) and a low difficulty score makes perfect sense. After you’ve consumed the list, then you can initiate targeting lower volume keywords.
3. Avoid keyword cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization is a situation when multiple pages fight to rank for the same keyword.
As experts note, the core problem protruding from keyword cannibalization is that it confuses the search engine. In fact, you are forcing them to select which page is more important taking that specific keyword amongst a group of other web pages. Eventually, the tendency to acquire traffic for that keyword diminishes.
Putting it simply, avoid writing a post associating a keyword that you already used in one of the inner pages or the homepage of your business website.
To eliminate the use of keyword cannibalization, enlist each page of your website along with the keywords you wish to pursue on a spreadsheet. Sorting the keyword column will help you catch the repetitive keywords.
Competitor research
Conducting keyword research is only half the journey, now comes the considerations for the competitor research.
1. The keywords your competitors are chasing
Gather the keywords you see your competitors have incorporated in their SEO strategy. You should even see if they have a higher Domain Authority (DA) and whether their web pages have more upper Page Authorities (PA) than you.
The required information can be collected from Moz’s free toolbar (the Meta data and header tags can be seen in the Page Elements tab, and PA and ranking details from the Link Data tab, respectively).
If your competition displays a better PA and DA than yours, obviously, it’s better to switch to other keywords as exhausting your time and effort will come to little or no avail.
2. The source of links your competitors are using
Another important thing is to uncover the places your competitors are using for inbound links.
Besides acquiring a link from these sites, you can also use blogger outreach, press outreach, or put up your own business pages.
After finalizing the list, the most important thing to do is to eliminate any link associated with a low DA score. Trying to get a link from a low DA website will most likely put you in Google’s bad books, the suspicion that a bad site is directing to your site will mean your site is percieved as unworthy too.
3. The architecture of your competitors’ sites
Inspect the architecture of the competitors’ website. Is the navigation seamless? How far do their links go? Any e-commerce businesses should particularly examine the architecture for flagship products in a specific category, related products, highly-sought after products and recently visited products. Consult some further questions like:
- Which search queries do visitors use before they get to their websites?
- Which search queries do visitors use when they are on their websites?
- Which pages on their websites call for the highest traffic?
- What are their top exit pages?
Once you acquire a generalized or focused idea of how the big names in the industry design their websites, you can either follow the course with the same designing specifications and technical details or opt for something unique.
Yes, it can be concluded that pages buried deep within a website find it very difficult to gain ample prominence in Google’s rankings. Therefore, promoting quality content up the site’s architecture is essential in order to elevate your overall rank in the search engine.
Looking from another perspective, if your direct competitors have employed a deeper navigational architecture on their websites, you aren’t bound to follow them just because they have some top products and a large visitor base.
4. Differentiating your website, from a strategic point of view
This consideration is more of an extension of the last point, seemingly, one of the crucial concerns remain:
What needs to be done to set you apart from the rest of your competitors in the e-commerce business?
You can break down the grand question by answering: Can the navigational architecture be improved? How can the website be made more social-friendly? Is your website aesthetically pleasing? Have you incorporated some or all of the trendiest design features? Do you plan to incorporate a blog? If yes, do you have a content marketing strategy in place?
Try to come up with additional, relevant questions for deciding what can be done to encourage more visitors to reach you rather than your competitors.
Final thoughts
But not the final phase in your SEO game! The research elements stage the platform where you start further work on the get-go.
There are additional steps in the ultimate guide of SEO for your e-commerce business which includes finding current issues in your website, on-page optimization, further testing, uploading blog posts, link building, and understanding the local business tips.
Mastering the research essentials is only where you start out in the race for securing the top spot in Google’s search results.