 If you are a small business owner with a grasp of what it takes to make your site rank for the search terms your potential customers use, great! But if you’re not, don’t despair. Many small business owners struggle with one or more aspects of search engine optimization (SEO), and for good reason.
If you are a small business owner with a grasp of what it takes to make your site rank for the search terms your potential customers use, great! But if you’re not, don’t despair. Many small business owners struggle with one or more aspects of search engine optimization (SEO), and for good reason.
While SEO is neither magic nor rocket science, it’s still fairly complex and getting more so every day. The vernacular can be somewhat confusing to everyone practicing SEO. Canonical, hreflang, schema, cache, robots.txt, .htaccess — these are just a handful of the many terms you’ll come across as you build, manage and market your website.
In this first of a three-part series, we’ll list and define some of the most common terms you’re likely to encounter while practicing SEO for a small business.
A
Above the fold – This is the content that’s visible to a website’s visitors before they scroll down. Obviously, it can vary, depending upon the device the visitor is using.
Algorithm – Often also referred to as an “algo,” this is a mathematical process or formula to execute a set of functions. For example, an algorithm determines which page in a search engine’s index is the best match for a given search query.
Alt attribute – This is the alternative text, encoded into a page’s hypertext markup language (HTML) or EXtensible hypertext markup language (XHTML), which should be displayed if an image or another element cannot be rendered in the browser.
Analytics – The information resulting from a systematic analysis of data or statistics, such as the number of visitors to a site, where they landed, where they originated and where and when they exited.
Anchor text – The clickable part of the link you see, often a keyword phrase, but can be a uniform resource locator (URL). Author Doc Sheldon is anchor text, as is www.searchengineland.com.
B
B2B– Business-to-business, when a business’s customers are other businesses.
B2C – Business-to-consumer, when a business’s customers are end-users.
Backlink – An incoming link to a web page from another webpage.
Blackhat – Often followed by the word “SEO,” blackhat most commonly refers to practices which are specifically designed to fool search engines into seeing a website as having more value than it really does, almost always in violation of the search engines’ webmaster guidelines.
Bounce rate – This refers to a percentage of visitors who leave a web page without interacting with it.
Bot – A piece of software which autonomously executes specific tasks according to preprogrammed inputs. This can include crawlers, chatbots or malicious bots.
Breadcrumb – This is a textual “map” of where a page is located within the hierarchy of a website. Breadcrumbs are normally clickable links, which can aid users in backtracking their steps. For example:
Home > About Us > Our Team.
Browser – This refers to a graphical user interface which displays HTML files and is used to navigate the Internet.
C
Cache – This is the storage of web content in memory, in order to be able to more readily serve them to a user. Caching commonly occurs on both servers and browsers.
Call to action (CTA) – A portion of the marketing message that tries to get a user to perform a certain action.
Canonical – This is an HTML element that indicates the original or preferred version of a piece of content, in order to avoid duplicate content issues.
CTR – Stands for click-through rate, the percentage of users shown an advertisement, search result or hyperlink who click on it.
Conversion – The conversion of a lead or prospect refers to the successful enticement of the user to complete the desired action, such as a purchase, download or subscription.
Correlation – This refers to an apparent relationship between two or more conditions wherein the relationship may or may not be interdependent. For instance, “When I stepped outside, I realized I was hungry.” Hunger was not brought on by having stepped outside.
Crawl – Web bots, also called crawlers or spiders, systematically crawl the internet, following links from one page to another, determining the connectivity that establishes the World Wide Web. If a page has no inbound links whatsoever, it will almost certainly never be found by the crawlers.
CSS – Refers to a cascading style sheet which is a file dedicated to telling browsers how a page should be displayed, in terms of font style, size and color. It also denotes the size, spacing and location of other HTML elements. It is a much more efficient method than inserting what may be highly repetitive data if inserted with each individual element.
D
Deep link – This refers to an inbound link to a page other than the home page of a website.
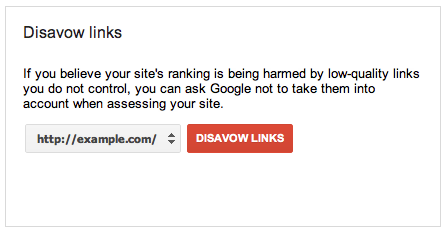
Disavow – At times, a site may receive inbound links from another web page of low quality or dubious character. If the site owner does not want these links and is unable to have them removed, the site owner may submit a disavow file listing the low-quality links via a disavow request. This is basically saying, “We prefer this link/domain be ignored.”
Domain – Each website has its own domain, which is part of its URL. In the URL for this page, the domain is searchengineland.
Duplicate content – This refers to blocks of content on a page which are identical or highly similar to content on another page, either on the same or another domain.
E
Entity – Entities are unique things which exist independently, such as people, places or things, so a company can also be an entity, as can a country or planet.
External link – This is an outbound link from a page to another page on a different domain.
F
Frames – Two or more documents are loaded independently and displayed on the same screen, each within a frame. It’s not advisable to use frames since search engine spiders have trouble navigating them.
H
Head – The head of a document contains elements such as the document’s title, metadata, scripts, styles and more. It will not contain any of the page’s content which is to be displayed.
Heading – In HTML, headings (H1 through H6) can be used to indicate the context of the content immediately following them in the hierarchy. They are generally used to emphasize titles or text on a page, with the H1 tag having the largest text.
For example:

hreflang – This refers to an HTML attribute that indicates to the search engines the language and geographic region for which the page’s content is intended.
.htaccess – This is a web server configuration file containing commands to direct the server’s behavior in certain circumstances. .htaccess is used by Apache servers and some other National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) compliant servers.
HTML – Hypertext markup language. This language is the heart of the Web, defining the content which is to be displayed and how it should be displayed.
HTTP – Hypertext transfer protocol. This is the protocol used across the World Wide Web, defining how messages are formatted and transmitted, as well as how servers and browsers should respond to various commands.
Hyperlink – This is a hypertext link between one point on the web and another. Clicking on a hyperlink will take the user to the destination point.
I
Index – The repository of pages a search engine has crawled and indexed, making them available for inclusion in the SERPs.
Information retrieval – The systematic process by which information is searched and extracted from the search engine’s index.
Internal link – These are hypertext links between two web pages of the same domain.
IP address – Internet Protocol address. A unique string of numbers separated by decimal points which identifies a device and serves as its address point on the internet.
J
JS – JavaScript. A text-based programming language used in web development to enhance web pages and make them more interactive.
K
Keywords – These are words which appear in the content on your web pages and are used in search queries. As search engines have evolved, matching a query to a term found in a document has evolved from exact match terms to synonyms to contextually relevant terms.
KPI – Key performance indicator. This is a measurable value that indicates the effectiveness of a business operation. It may include such factors as gross profit margin, cash flow, market share, inventory turnover and more.
L
Linkbait – A piece of content created to attract inbound links.
Link profile – This aggregate presentation of all of a site’s inbound links presents the search engines with an image of the site’s value, as perceived by other sites.
Log file – A file that records web server activity.
M
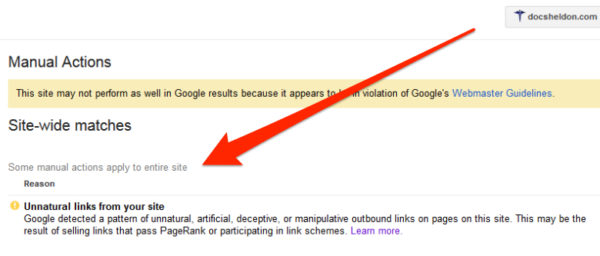
Manual action – If during a human review, a web page or site is determined to be in violation of the search engine’s webmaster guidelines, a manual action may be implemented which will have a detrimental effect on rankings. These actions can affect a single page or may be applied across the entire domain.
Metadata – This is a set of data that is not always displayed by the browser which provides information to the search engines about other data on the page.
N
Nofollow – At times, it may be considered necessary or even helpful to link out to a resource which is of questionable veracity or dubious quality. Adding a nofollow attribute to a hypertext link essentially tells the search engines that you don’t vouch for the target page.
Noindex – This meta tag can be added in a document’s head to tell the search engine that the page should not be allowed to appear in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
O
Organic – This refers to search results which do not include any paid advertising.
Outbound link – A link sitting on a web page which links to a page not found on the same website.
P
PageRank – This is a calculation to determine the overall quality of a page, based upon many factors, the most important of which is still considered to be inbound links.
Panda – This was a new search algorithm, launched in February of 2011, which focuses on detecting low-quality or “thin” content.
Penguin – This algorithm, launched in April of 2012, focuses on the quality of inbound links.
PBN – Private blog network. Interlinked websites owned by the same entity. Some PBN’s are considered manipulative because they exist to host content and links as a way to influence the SERPs. Once a highly effective technique, it has become increasingly difficult for such networks to avoid detection.
R
RankBrain – This algorithm, confirmed by Google in October of 2015, is a machine-learning algorithm which examines search queries the search engine has never seen before and attempts to correlate them with queries it already knows.
Reciprocal link – Two web pages on two different sites link to each other on purpose. Large numbers of reciprocal links can be seen as manipulative linking schemes if the links are placed for the sole purpose of influencing the way a web page ranks.
Redirect – This is a technique by which a hyperlink to a destination URL is redirected to a different URL. The most commonly used redirects are 301 (permanent) and 302 (temporary), although there are others which are rarely used. (See Status Codes)
Responsive – One method of site design which resizes the displayed elements to suit the viewport of the device viewing the site. Thus, a site can be easily viewed and read from a desktop, tablet or phone.
Rich snippet – By using structured data markup, such as schema, microformats or Resource Description Framework in Attributes (RDFa), small samples of a site’s content can be shown in the SERPs, often enticing more users to click through to the site.
S
Schema – This is a semantic markup involving specific ontologies which classify objects and shows the relationships between them.

Search Console – previously called Google Webmaster tools, is a suite of free services from Google to check indexing status and optimize a site’s visibility.
SERP – Search Engine Results Pages. Web pages of ranked results provided in response to a search query.
Server logs – One or more automatically generated logs of all actions performed by the server, often helpful in determining what caused a problem to occur.
Server side includes – Also known as SSI. A way to retrieve portions of a page from another web page.
Sitelinks – These appear in some results in the SERPs, where numerous internal links are provided, making it easier for users to navigate directly to the portion of the site that interests them.
Sitemap – A hierarchical model of a website’s content, typically constructed in HTML, to aid users in navigating the site to inform the search engines of the site’s content.
Sitewide – This refers to linking and navigational structure that is employed on every page of the website, such as in the sidebar or footer.
SSL – Abbreviation for Secure Sockets Layer. This is the standard technology for establishing an encrypted pipeline between the client (browser or email client) and the server.
Status code – Numeric responses given by web servers in response to a call from a browser. Each different numeric code signifies something different.
Subdomain – An internet domain which is part of a primary domain. For example, in the URL https://blog.searchengineland.com/, ‘blog‘ would be a subdomain of the primary domain searchengineland.com.
T
Taxonomy – this refers to a system of classification and is particularly important in faceted navigation such as is normally present in an e-commerce site.
Title tag – HTML that creates the title of a web page and generally tells humans and search engines what the page is about. It is located in the section of a web page and what (usually) shows up in the search engines organic results.
TLD – Top-level domain. This is the general classification of all domains under the TLD. For instance, .com, .net, .org and .edu are all TLDs, although there are now many others.
U
UGC – User-generated content. Content on a web page which is created by users, rather than by the site owner or webmaster. Forums and blog comments are both forms of user-generated content.
Unique visitors – People (searchers) who have visited a web page once during a specific period of time.
URL – Uniform Resource Locator. Sometimes called the web address. For this site’s home page, the URL is https://searchengineland.com. However, that’s not the actual address. The URL is translated to our IP address, 208.80.6.139, by the domain name server.
User-agent – Every user on the internet has its own user agent, browsers, clients, crawlers, even feed readers and media players. The user agent identifies the user to the server, which, in turn, identifies itself back to the user via its own user agent.
V
Vertical search – Refers to a type of specialized search that returns results from a specific area.
Vlog – A blog in video form.
W
Webmaster Guidelines – These are guidelines are published by search engines, describing behaviors and practices which the search engine considers to be acceptable. Failing to comply with those guidelines can result in a loss of rankings or punitive action.
White hat – This is commonly believed to imply following only practices which are deemed acceptable under the published Webmaster Guidelines.
Widget – An element of a graphical rather than a textual user interface that prompts users to act or displays information. It is usually a stand-alone element that can be embedded in a web page as an advertisement or interactive experience. Google frowns on using widgets like this one as linkbait :

X
XHTML – eXtensible Hypertext Markup Language. A language which reformulates HTML 4.0 in XML syntax.
XML – eXtensible Markup Language. This markup language uses a different syntax from HTML and considerably extends the vocabulary available with HTML.
While the above listing is by no means an exhaustive list of terms you’ll encounter in your SEO adventures, they should help you avoid being bewildered by a flurry of buzzwords. Hopefully, they’ll clear up some questions you may have had.
Status Codes
301 – The URL has moved permanently. When you want to change the URL of a web page listed in the search results, use a 301 redirect.
302 – Known as a temporary redirect.
403 – Forbidden. The server refuses action even though the request is valid.
404 – Not found. The page/resource is not found.
503 – A server is down for maintenance or because of too many requests, usually a temporary state.
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
