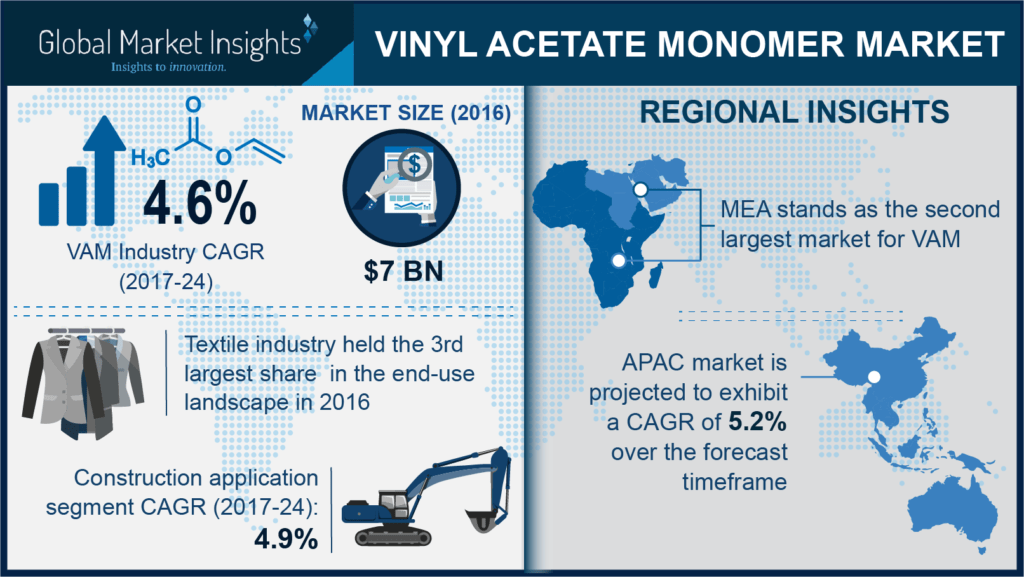
Over the last few years, vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) industry has emerged as a highly viable investment avenue, attracting myriad financial backers owing to its escalating use as a chemical intermediate. The incredible end-products that can be manufactured using VAM as a primary ingredient span the polymers space – polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl acetate, and vinyl chloride copolymer. Given the widespread usage of these polymers in the formulation of laminate films, adhesives, paints, cosmetics, and lacquers, it is now rather overt that the growth prospects of VAM industry are directly proportional to the expansion of the humongous polymers sphere. Uflex for instance, recently unveiled a 2K solvent-based PU laminating adhesive under the Flexbon brand in the polymers industry, validating how the rising developments in this space would widen the scope of VAM.
It is also noteworthy to mention that the widespread applications of VAM have had a significant impact on acetic acid market, primarily since acetic acid is one of the basic raw materials to manufacture VAM. Indeed, reliable statistics state that in 2014, more than 30% of the overall production of acetic acid had been consumed for the production of VAM. The product forms a pivotal part of the application spectrum of acetic acid industry, on account of the fact that it is widely deployed to manufacture resins for myriad end-use domains. As per estimates, acetic acid market size is anticipated to cross USD 16 billion by 2024, at an appreciable CAGR of 8.7% over 2017-2024. This precisely validates that the development of this industry is certain to impact VAM market trends.
Attesting to the incredibly massive application spectrum of vinyl acetate monomer industry, core companies have been undertaking numerous initiatives to enhance their production capacity. Geographically, most of the VAM manufacturers have already established their business across U.S. and European countries including Germany, France, Belgium, Italy, and Spain, however, the tactic seems to have been strengthened even more in recent times. Citing an illustration, a few years ago, Sipchem (Saudi International Petrochemical Company), headquartered in Saudi Arabia, acquired Acetyl Complex, the subsidiary of the Kuwait based Ikarus Petroleum Industries Company located in Saudi Arabia. With this acquisition, Sipchem has substantially increased its production capacity of acetic acid and vinyl acetate monomer, conveniently expanding its position across the Middle East. In addition to acquisitions, many biggies have also been ramping up their efforts to set new benchmarks in terms of reliability, performance, and quality of products in VAM industry through myriad innovations and technology developments.
Pricing has been a slightly disturbing concern for VAM manufacturers for quite a while. A few years ago, on account of supply demand mismatch, VAM prices observed an unexpected surge, especially in the U.S. In the year 2014, the limited regional supply of chemical compounds in the country led to increased prices of VAM and its derivative products. However, the average sales of refining products led to a demand-supply gap, that ironically helped vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) industry stay afloat. One of the principal reasons for the same is the robust demand for derivative products of VAM that find usage in numerous applications such as paper finishing, printing inks, adhesives for construction and packaging, water-based paints, and textile fibers. (Refer to Table 1 for more details)
A couple of application arenas that have proved as viable revenue generating grounds for VAM manufacturers have been enumerated below:
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) ?Growing demand from numerous sectors to push VAM industry trends
Manufactured from the polymerization of vinyl acetate monomer, PVA is a synthetic resin that possesses numerous properties such as creep resistance, higher strength, water-resistance, remarkable setting speed, and excellent adhesiveness. On these grounds, PVA is primarily used as an adhesive and film forming agent in water-based paints. In addition, the product seems to have found deployment in the construction sector as a woodworking glue. One of the most unique instances demonstrating the effectiveness of PVA as an excellent binder is when it had been liberally used to ready the cricket pitch for the ICC Champions Trophy match in 2006. Incidentally, the usage of PVA back then had prevented the pitch from disintegrating and had imparted it with long-lasting surface quality, paving the way for VAM industry players to make investments in the construction sector where PVA would be used abundantly. It would be rather fair to quote in this case, that the deployment of PVA adhesives would also have a consequential impact on adhesives and sealants market share. For the record, in 2015, PVA-based adhesives and sealants industry held a valuation of 2.5 million tons in terms of volume.
Taking into account the effectiveness of PVA as a binding material for woodwork, many researchers are working continuously to improve its applicability by enhancing its shear strength. Additionally, polyvinyl acetate is also used in water treatment and in many cases, as an effective coating agent. The permeable use of PVA for binding, coating, and sealing would thus prove highly lucrative for impelling vinyl acetate monomer industry share in the ensuing years.
Table No: 1 Vinyl acetate derivative and its application spectrum
|
|
|
Applications of VAM
| ||||
|
|
|
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA)
|
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA)
|
Vinyl acetate ethylene (VAE)
|
Vinyl acrylic co-polymer
|
Vinyl chloride co-polymer
|
|
End-use Spectrum
|
Paint
|
✓
|
–
|
✓
|
✓
|
–
|
|
Adhesive
|
✓
|
✓
|
✓
|
–
|
✓
| |
|
Printing ink
|
✓
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✓
| |
|
Film
|
–
|
✓
|
–
|
–
|
–
| |
|
Lacquer
|
✓
|
–
|
–
|
–
|
✓
| |
|
Building material
|
✓
|
–
|
✓
|
✓
|
–
| |
|
Textile finishing
|
✓
|
–
|
✓
|
✓
|
–
| |
Vinyl acetate ethylene (VAE)?Regulatory support and business expansions to bring forth new avenues for Europe vinyl acetate monomer market
The use of vinyl acetate ethylene, one of the prominently preferred derivatives of VAM, is highly encouraged owing to its safety, versatility, and performance. Incidentally, since VAE-based packaging solutions can be manufactured without the use of any organic solvents, they are extensively used for paper and packaging purposes. Thus, amidst the current scenario that depicts the adoption of sustainable and environment friendly binding and packaging technologies, the use of vinyl acetate ethylene has commendably risen.
Another pivotal factor promoting the growth of VAM industry from the use of vinyl acetate ethylene is the presence of a strict regulatory landscape revolving around food packaging and plastic manufacturing. In order to protect the environment, the EU has recently undertaken an initiative to encourage the deployment of recyclable packaging and plastic solutions. The organization aims to save investments in waste sorting through this initiative, in addition to helping companies develop recyclable and smart plastic materials via substantial funding.
An instance validating the massive use of vinyl acetate ethylene – by extension, VAM as a whole, across myriad end-use domains throughout Europe is that of INEOS’s investment. The leading chemical major, in 2017, spent millions of Euros in Europe to construct a vinyl acetate monomer plant of 300 Kiloton production capacity. This investment is likely to further catapult INEOS’s position in Europe VAM industry, given the humongous demand for high-performance films, adhesives, car fuel tanks, and windscreens across Europe. The initiative also paved the way for numerous regional VAM manufacturers to explore further expansion opportunities across the continent.
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA)?Investments in solar infrastructure developments to stimulate vinyl acetate monomer industry trends
Currently, ethylene vinyl acetate is emerging as a viable alternative for conventional polymeric materials owing to its notable characteristics such as resistance to rupture, softness, high flexibility, inertness against chemicals, and excellent adhesion. On these grounds, EVA films, manufactured from the copolymer of ethylene vinyl acetate, have been extensively used to develop laminated films that are used for safety glass construction. Additionally, EVA films find usage in fire safety and UV rays protection as well. Considering the vast expanse of the construction industry, that paves way for the aforementioned applications to flourish, VAM manufacturers have been working tirelessly toward capacity expansions, that would help generate a cost-effective environment in vinyl acetate monomer industry.
An incidence providing testament to the efforts of VAM manufacturers to improve the production capacity is that of Dow’s plant set up. In 2012, the chemical magnate, Dow Chemical Company, had established two new EVA film manufacturing plants. Post this initiative, Dow had been able to triple its manufacturing capacity of specialty films used in photovoltaic modules. The launch was an apt example underling the fact that capacity expansions would majorly aid the growth of VAM market.
The extensively developing inter-continental strategic relations among nations with regards to green infrastructure have also contributed their bit toward impelling vinyl acetate monomer market share. For instance, recently, South Korea signed a bilateral cooperation agreement with Saudi Arabia to develop renewable, nuclear energy, medical, and technology infrastructure across the Middle Eastern nation. South Korea has also invested in the development of solar energy infrastructure in Saudi Arabia. What’s more, Saudi Arabia has already witnessed an investment made by Hanwha Chemical, a South Korea based chemical company, for manufacturing around 4000 tons of ethylene vinyl acetate films per annum that would be used in solar panel lamination. It is thus rather overt that Saudi Arabia, in the ensuing years, will prove to be a remunerative investment destination for VAM manufacturers.
The application array of vinyl acetate monomer will indeed have a commendable trace on VAM industry outlook. Furthermore, with the consistent adoption of tactics such as strategic new product development and facility expansions, companies are likely to garner the advantage of lucrative revenue generation opportunities. Despite the fact that the global competitive scenario of this space is rather fierce, the enforcement of foreign direct investment policies will tend to improve the situation in the regional VAM market.
Of late, analysts are of the view that the shifting trends toward green infrastructure, primarily solar-based systems, will bring about a transformative change in the VAM industry across Middle East and European countries. Given the extensive deployment of this product across the packaging, automotive, construction and numerous other sectors, aided by a strong regulatory frame of reference, Global Market Insights, Inc., forecasts vinyl acetate monomer industry size to be valued at over USD 10 billion by the end of 2024.
Global Market Insights, Inc. has a report titled “Vinyl Acetate Monomer (VAM) Market Size By Application (Polyvinyl Alcohol, Polyvinyl Acetate, Ethylene Vinyl Acetate, Vinyl Acetate Ethylene, Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol), By End User (Packaging, Construction, Textile, Cosmetic), Industry Analysis Report, Regional Outlook (U.S., Canada, Germany, U.K, France, Spain, Italy, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Brazil, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, UAE), Growth Potential, Price Trends, Competitive Market Share & Forecast, 2017 – 2024” available at
https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/vinyl-acetate-monomer-vam-market