It’s the 21st century. Businesses are moving online and with terabytes of data.
According to a study, the big four companies Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and Facebook store 1,200 petabytes between them, which is equivalent to 1.2 million terabytes, where one terabyte is 1,000 gigabytes.
The huge amount of data has made cyber attacks an imminent event. And one of the most threatening pathways of a cyber attack is malware.
Malware (malicious software) attacks are on the rise. According to the 2018 Internet Security Threat Report of Symantec, the number of malware variants increased by 54% in 2017.
According to the 2019 Internet Security Threat Report from Symantec, cyber-criminals using malware increased by 25%. This is clearly an area that requires focus from businesses and government. Otherwise, its effects could be devastating.
How Does Malware Impact Cybersecurity?
Malware is a file or program that may harm the computer user, and cause the breach of data security.
Malware includes a variety of types like:
- Ransomware
- Spyware
- Command and control
- Virus
- Worms
- Trojan horse
What Does Malware Do?
They usually result in a few established outcomes:
1. Data Exfiltration
Malware usually takes control of the computer without user consent. And after taking control, it can filter out essential business data, client data, and even personal data, without any knowledge of the user.
It is essentially a form of data theft, which can be very costly. According to a study by Ponemon, the global average cost of the data breach has risen by 6.4% from 2017 to $3.86 million. Apart from business disruption, this can tarnish the image of the company, and hamper customer goodwill.
2. Operations Disruption
Cyber-security ensures the smooth running of digital operations of a business. But a malware attack can wholly or partially disrupt it. The levels of disruption may vary in scale.
It may range from a virus corrupting crucial Operating System on one system, to disrupting whole networks of systems. One of the best examples of the latter is Stuxnet, a malicious computer worm, capable of bringing down whole networks.
It has larger ramifications, sometimes in the form of DDoS attacks. For example, a DDoS attack can completely shut down your website in less than a minute. And no website is immune to it. For instance, the 2016 Dyn cyber-attack paralyzed PayPal and Twitter.
If proper security measures are not in place, such business disruptions cause an enormous loss in revenue for the down-time.
3. Money Extortion
If the malware finds its way past your cyber-security, one of the reasons could be extortion of money. To this end, Ransomware is particularly important. It basically freezes your access to your date until you pay up a certain demanded amount.
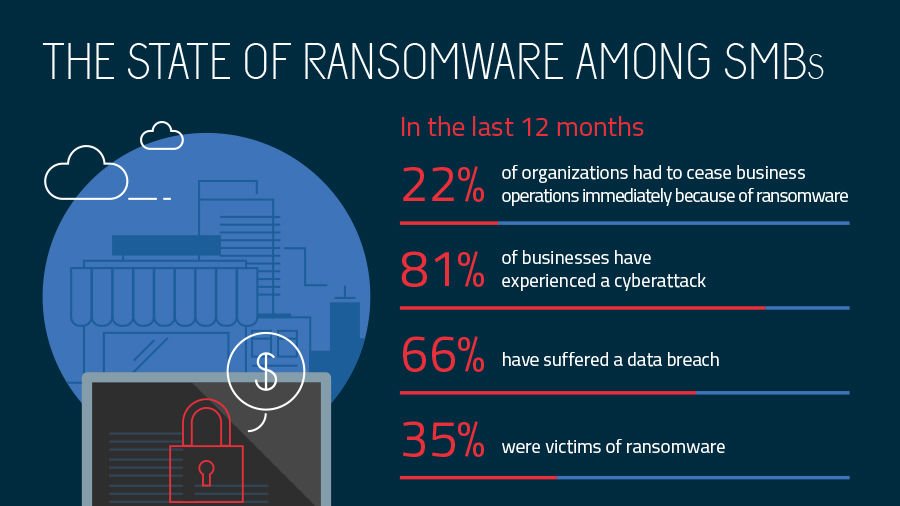
Have a look at these pertinent statistics:
(Image: Source)
This is a depiction of ransomware affecting small and medium businesses in the US.
And these types of attacks are evolving. Reveton, one such ransomware, accused their targets of child pornography and other illegal activities and held them to ransom until they paid up.
4. Keystroke mapping and account access
This is a malware attack by Trojan, that is very simple, yet can have deadly consequences. It targets you as you type in sensitive information into your computer, like the details of your bank account.
By shadowing you, it records the keystrokes you made and goes on to steal your credentials. It can then access and take out money from your account without any consent.
This has been used to great effect by Zeus malware, a form of Trojan that does excellent keystroke mapping.
5. Sending out spam
So, consider this scenario:
Recently your clients tell you that they have been receiving a lot of spam from you. You are quite taken aback. But you should also know, this is a clear indicator of you being infected by insidious malware, which has got past your cyber-security. To be more precise, it’s spyware!
Spyware infiltrates your computer and gains access to your internet usage data. It can hand the cyber-criminals your official business social media login credentials, and they may try to destroy your image by propagating malicious intent using your credentials. Such types of sensitive data can be hazardous in the wrong hands.
You must ensure your computer is free from malware, and take the necessary precautions. Beef up your IT security and run regular malware scans to keep your system healthy.
6. Deleting Entire Files
Malware can go above and beyond your cyber-security protocols to delete very sensitive and important business files.
New malware deletes entire files, while they claim that the files have been moved to another location for additional security (without your knowledge).
For a token payment, they guarantee that your account will be released to you. In reality, the files have been deleted or infected irreversibly, so that retrieval is well-nigh impossible.
One of the recent examples of such malicious malware is Nukeware. It asks you to pay the ransom, although there is no way to recover your files.
Events like this can significantly affect your cyber-security measures and undermine them.
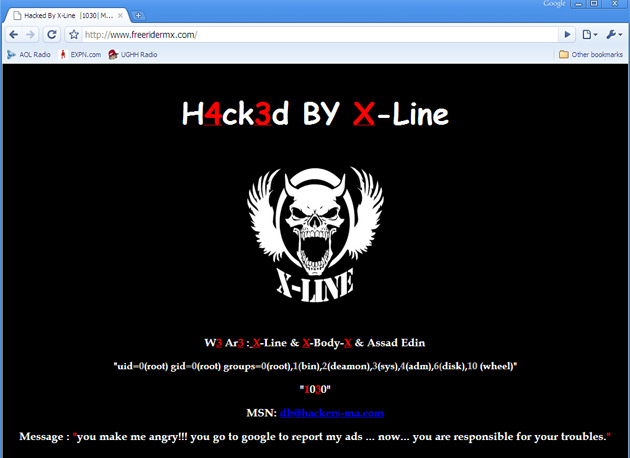
7. Website Defacement
This is a big problem in the current era of online businesses. Defacements allow cyber-criminals to gain editing access to the website, and they can delete or modify the website content. They may even replace the website’s words with their own message, usually promoting and highlighting religious agenda.
The defacement can have serious implications on the reputation of the business and may cause monetary repercussions, as clients may be dissuaded to conduct further business with them.
Here’s an example of website defacement:
(Image: Source)
It may even prevent others from accessing your website. The problem is very common. In fact, according to a study, defacements accounted for 14% of all attacks in Q2 of 2018 alone. In fact, without the right security in place, these may be able to paralyze cyber-security protocols as well.
Wrap-Up
According to a study, websites experience up to 58 attacks per day. This is equivalent to at least one cyber attack every 25 minutes.
Clearly, the problem of cyber-security is compounding and cannot be ignored anymore.
Cyber-criminals are getting smarter, and cyberattacks are getting even more prevalent than ever before. If statistics are anything to go by, even the search engines are still blacklisting, only 17% of websites infected with malware.
One of the best ways is to educate your employees so that they can assist you in this fight against malware attacks. Moreover, it’s a great idea to encourage them to get cyber security certifications to arm themselves against such malicious online attacks.
Malware is evolving. It’s time our cyber-security methods did, too.
Image: Depositphotos.com